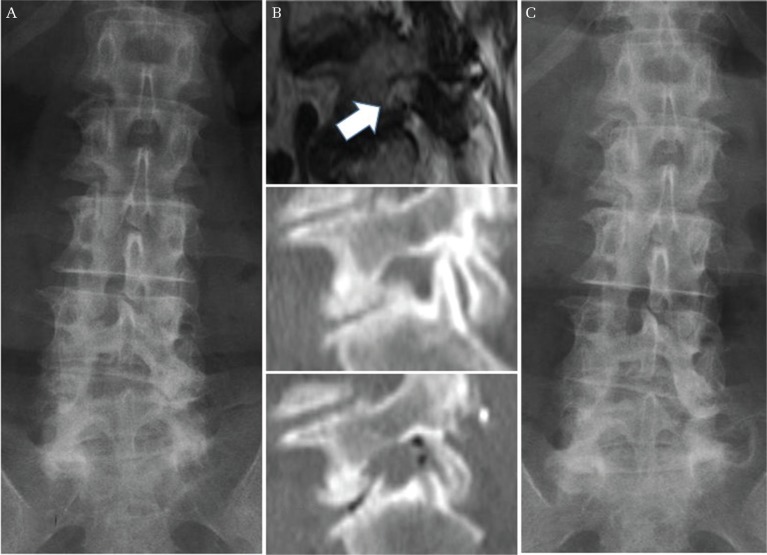
Fig. 3.
A representative case of recurrence of LFS due to progression of disc wedging. A 67-year-old woman underwent a lateral foraminotomy for left L5/S foraminal stenosis. Her preoperative radiograph showed 8.2° of disc wedging at L5/S concave to the left (A). Her MRI and CT demonstrated circumferential stenosis of the left neural foramen at L5/S, and sufficient decompression was achieved after surgery (B) (upper; preoperative MRI sagittal image, middle; preoperative CT sagittal image, lower; postoperative CT sagittal image, white arrow demonstrates narrowed neural foramen). 14 months after the initial surgery, she underwent a revision TLIF because of recurrent radiculopathy. At the time of recurrence, her radiograph showed significant progression of disc wedging at L5/S, measuring 9.6° concave to the left (C). LFS: lumbar foraminal stenosis, MRI: magnetic resonance imaging, CT: computed tomography, TLIF: transforaminal lateral interbody fusion.