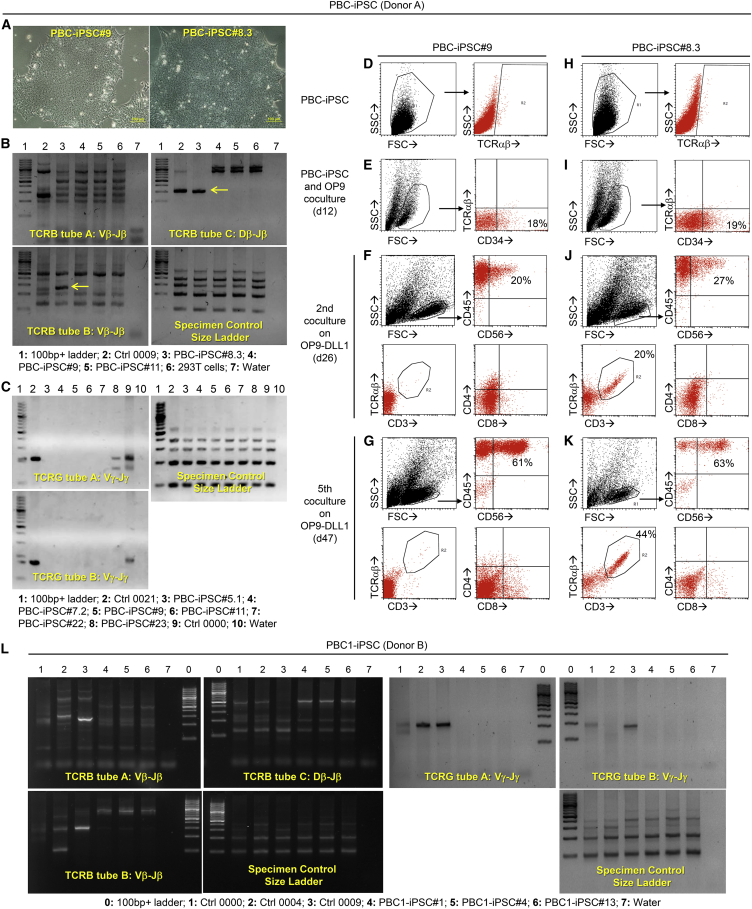
Figure 2.
Generation of PBC-iPSCs for Production of NK Cells
PBCs from different donors were used to generate various PBC-iPSC lines. Results were obtained using PBC-iPSC (donor A) lines (A–K) and PBC1-iPSC (donor B) lines (L).
(A) Morphology of two PBC-iPSC (donor A) lines, PBC-iPSC#9 and PBC-iPSC#8.3.
(B and C) TCRB gene (B) and TCRG gene (C) clonality assays to detect rearranged TCRβ and TCRγ chain genes in PBC-iPSC (donor A) lines. Positive amplified product is indicated by the yellow arrow.
(D–K) Production of NK cells from two PBC-iPSC (donor A) lines, PBC-iPSC#9 and PBC-iPSC#8.3. (D–G) Phenotypic changes during differentiation of non-T cell-derived PBC-iPSC#9 line into NK cells. Flow cytometric analysis shows no TCRαβ expression during differentiation. (H–K) Phenotypic changes during differentiation of T cell-derived PBC-iPSC#8.3 line into NK cells. Flow cytometric analysis shows re-expression of TCRαβ during differentiation.
(L) TCRB gene and TCRG gene clonality assays to detect rearranged TCRβ and TCRγ chain genes in PBC1-iPSC (donor B) lines.