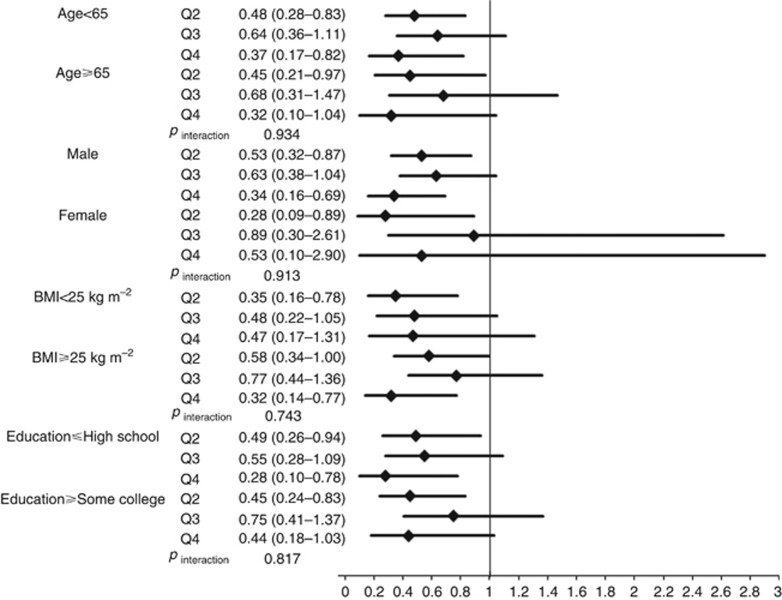
Figure 3.
Impact of higher quartiles of food folate intake (Q2, ⩾261.36 to <350.41 μg per day; Q3, ⩾350.41 to <460.90 μg per day; Q4, ⩾460.90 μg per day) on HNC risk compared to the lowest quartiles of food folate intake (Q1, <261.36 μg per day) according to selected covariates. The hazard ratios (HRs) were estimated from Cox proportional hazard models, adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, education, race/ethnicity, pipe smoking status, cigar smoking status, pack-year cigarette smoking, alcohol drinking intensity, non-alcohol total energy, total vegetable and fruit intake. We found no interaction between selected covariates and total fibre intake on HNC risk.