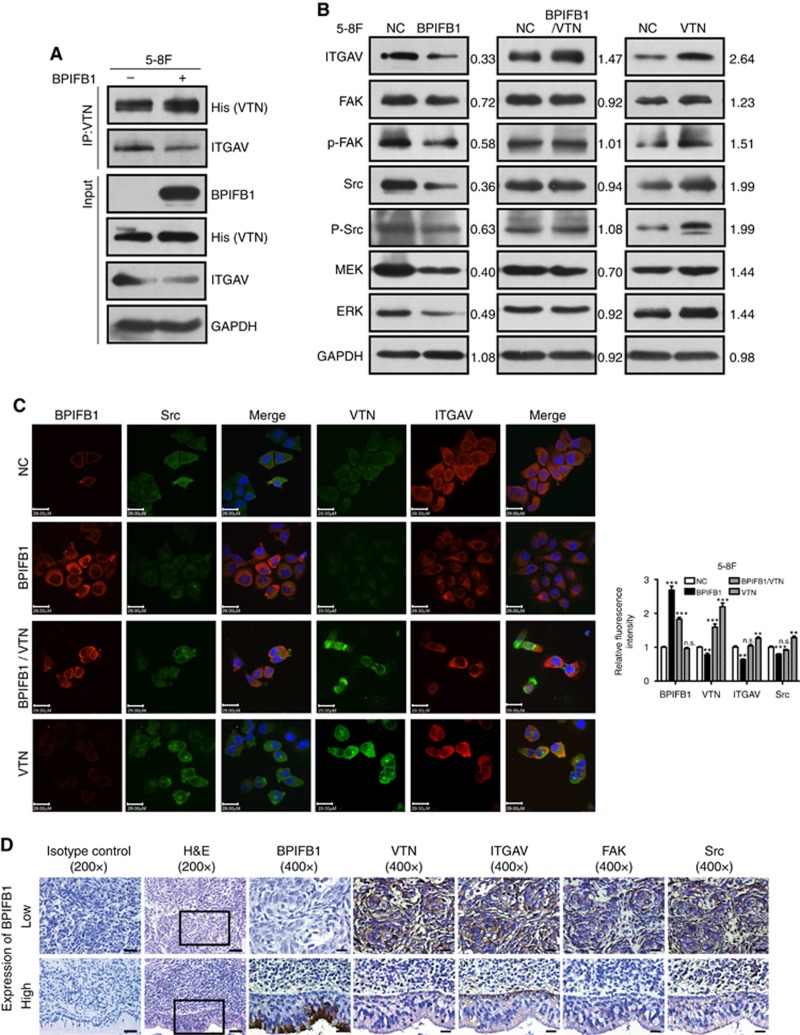
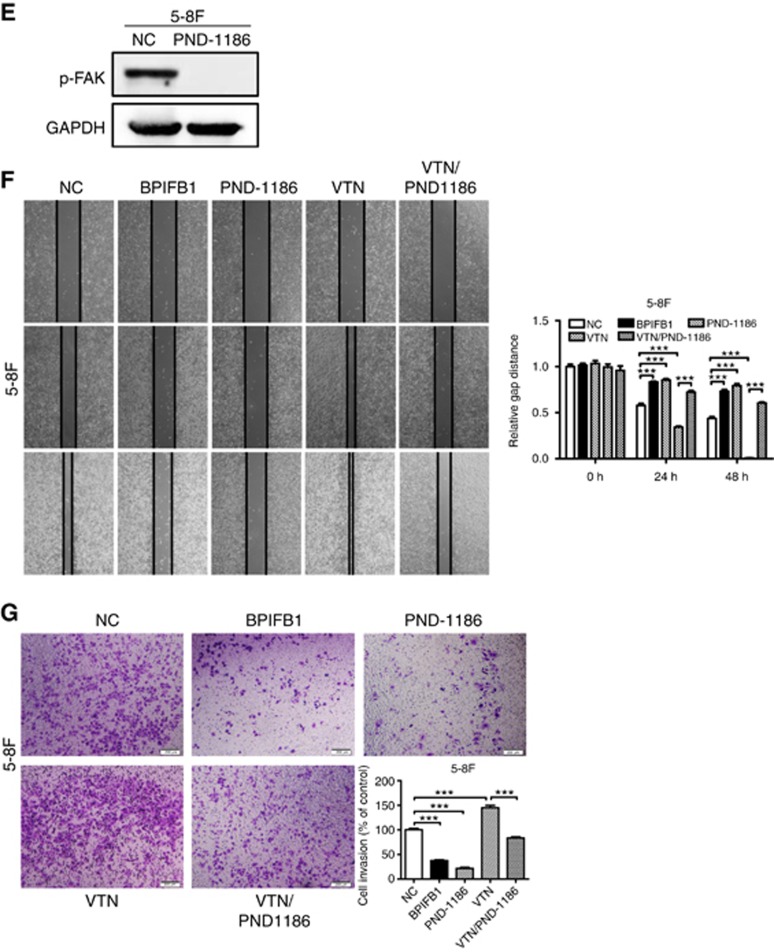
Figure 5.
BPIFB1 inhibits VTN-ITGAV-complex formation and downstream activation of the FAK signalling pathway. (A) The ITGAV protein was immunoprecipitated by the VTN antibody in 5-8F cells. (B) Expression of ITGAV and some proteins associated with the FAK-signalling pathway, including FAK, p-FAK, Src, p-Src, MEK, and ERK, was detected by western blot in 5-8F cells transfected or co-transfected with BPIFB1-Flag and VTN-His vectors. (C) BPIFB1, VTN, ITGAV, and Src expression was detected by immunofluorescence in 5-8F cells transfected or co-transfected with BPIFB1-Flag and VTN-His vectors. Scale bar=29 μm. Five randomly selected areas were scanned, and the data are shown as the mean±s.d. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; n.s., no significance. (D) BPIFB1, VTN, ITGAV, FAK, and Src expression as determined in 20 NPC and 11 NPE tissues by immunohistochemistry. H&E staining was also performed on these tissues. Data shown are representative images of the respective molecular expression analyses. Normal rabbit immunoglobulin G was used as the isotype control. Magnification= × 200, scale bars=50 μm; Magnification= × 400, scale bars=20 μm. (E) Administration of the FAK inhibitor PND1186 decreased p-FAK expression. (F and G) PND1186 suppresses NPC cell migration and invasion in 5-8F cells induced by BPIFB1 loss or VTN overexpression. The graph summarises data from three independent experiments. Scale bars=200 μm.