Fig. 2.
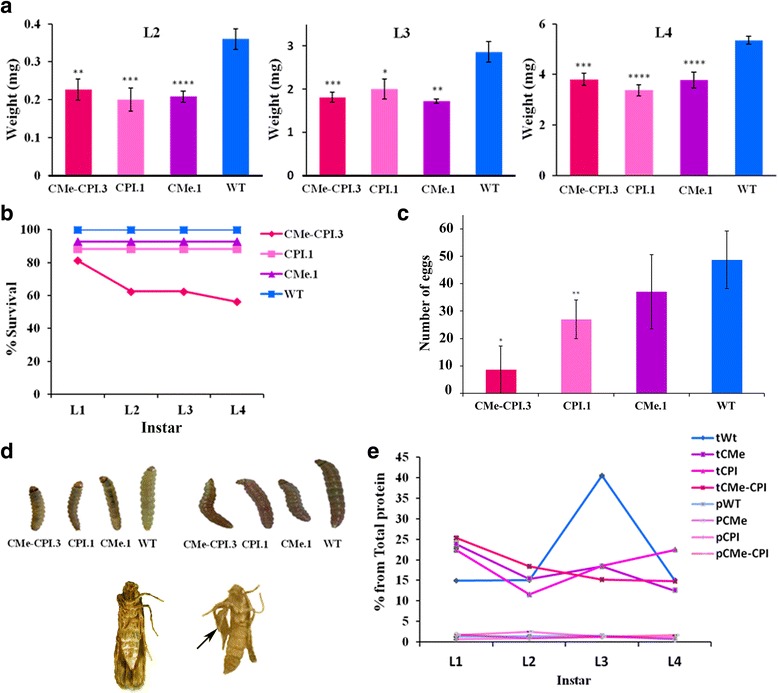
Tuta absoluta feeding trials. a Larvae weight when fed with the three transgenic plants and the wild type. Larval weight is reduced in all larvae fed with the transgenic leaves. Statistical test: t test, n = 8, significance p < 0.05. b Larval survival decreased with the increasing number of feeding days reaching 56.25% (Chi test, p = 0.018) for the CMe-CPI.3 transgenic line. The first and second instar showed the highest mortality level. c Number of eggs laid after 48 h. Decrease in the number of eggs for adults emerged from larvae fed on the different transgenic lines, mostly CMe-CPI3. (n = 5, t = 2.54, df = 7, p = 0.022). d Morphological alterations. Upper left: L3 larvae fed with transgenic and wild type plants. Larvae fed with the three transgenic plants show reduced size; Upper right: L4 larvae fed with transgenic and wild type plants; larvae fed with the three transgenic plants show reduced size; Bottom left: Adult female emerged from a larva fed with WT plants; Bottom right: Wing deformity observed in a female adult emerged from a larva fed with transgenic plants (arrow). e Trypsin and papain activity in insects’ crude extract. Trypsin-like and papain-like activity decay in larvae fed with the different transgenic plants when compared with wild type. t: refers to trypsin and p: refers to papain
