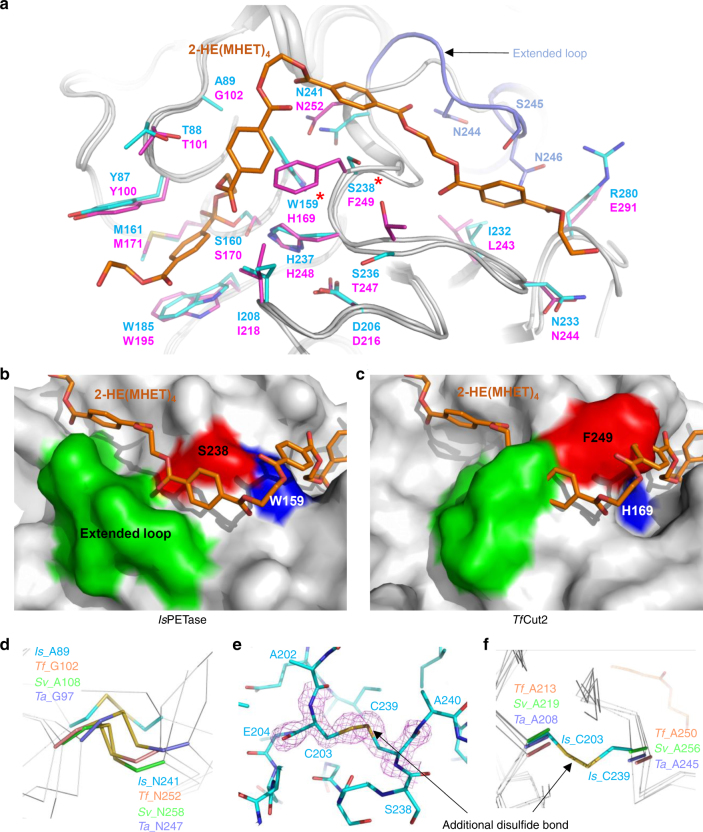
Fig. 5.
Structural comparison of PET-degrading enzymes. a Superposition of the structures of IsPETase and TfCut2. Both structures of IsPETase and TfCut2 are shown as gray-colored cartoon model. The 2-HE(MHET)4 docking model of IsPETase is shown as an orange-colored stick. Residues constituting subsite I and subsite II of IsPETase and TfCut2 are shown as a line models with cyan and magenta colors, respectively, and labeled. The unique residues observed in IsPETase, Trp159 and Ser238, are indicated with star marks. The extended loop of IsPETase distinguishable from TfCut2 is shown in light-blue color. b, c Structural difference on subsite II of IsPETase (b) and TfCut2 (c). The structures of IsPETase and TfCut2 enzymes are presented as surface models with a gray color. The 2-HE(MHET)4 docking model of IsPETase is shown as an orange-colored stick. The Ser328 and Trp159 residues in subsite II and extended loop of IsPETase corresponding phenylalanine and histidine residues and extended loop in other PET-degrading enzymes are distinguished and labeled, respectively. d Disulfide bond found in PET-degrading enzymes. The disulfide bond found in each all four PET-degrading enzymes is shown as a stick model, respectively and the residues forming the disulfide bond are labeled. e, f Additional disulfide bond found in IsPETase. The IsPETase structure is presented as a stick model and the omit electron densities (magenta mesh) of the residues constituting the additional disulfide bond in IsPETase are contoured at 2.0 σ (e). The additional disulfide bond region in IsPETase is compared with the corresponding regions in other PET-degrading enzymes (f). The residues forming the additional disulfide bond in IsPETase and those located at the corresponding positions in other PET-degrading enzymes are shown as a stick model and labeled appropriately