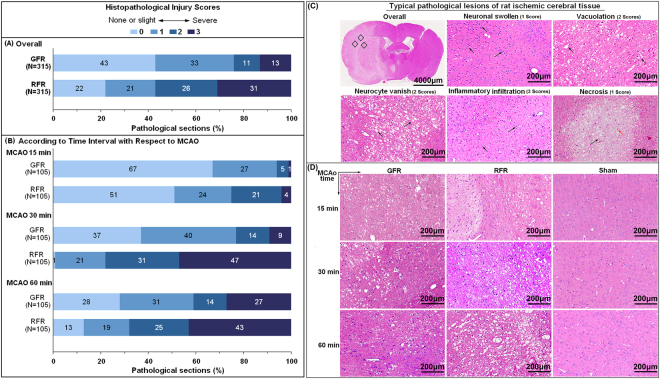
Figure 5.
Histopathological injuries of cortex in MCAO rats undergoing GFR and RFR intervention. After assessment of neurological deficit score, brains were removed and fixed in 4% neutral paraformaldehyde. Then, the brain tissues were embedded in paraffin and sectioned at 4 μm thickness in the coronal plane. The sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E), and examined under light microscopy (magnification 200×). The histopathological damages were quantified by scoring the extents of the total lesion including focal cerebral edema, vacuolation, neuronal vanish, inflammatory infiltration as well as neuronal necrosis with a scale of 0–3. (A) Overall histopathological lesions score in MCAO rats undergoing GFR and RFR. (B) Histopathological lesions score according to time interval with respect to MCAO. Data were presented as a percentage of the number of sample in each score to the total numbers of corresponding samples. Significance was determined by Wilcoxon rank-of-rank tests. (C) Typical pathological lesions of rat cerebral issue. Red arrow represents photo site of typical inflammatory cell infiltration; black arrows represent each of these typical pathological lesions. Scores of the histopathological lesion are 1 score for neuronal swollen and necrosis, 2 scores for vacoulation and neurocyte vanish, and 3 scores for inflammatory infiltration, respectively. (D) Histological changes of cortex in MCAO rats undergoing GFR and RFR. Photomicrographs showed more significant neuronal damages and inflammatory infiltrations in the RFR group than in GFR group, in contrast with no notable morphological changes in sham group. Scale bar = 200 μm.