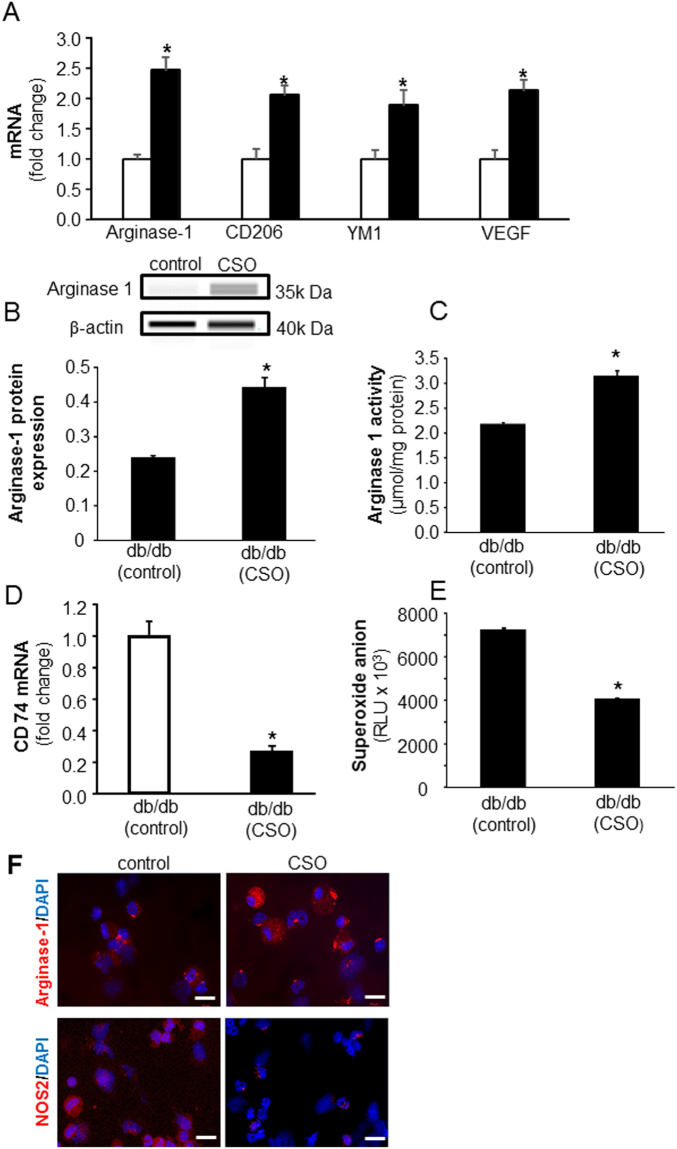
Figure 4.
CSO is a potent inducer of mϕheal macrophage polarization while attenuating M1 phenotype in chronic diabetic wounds. (A) Wound mϕ were harvested from PVA sponges coated with CSO (300 mg) implanted subcutaneously in db/db mice on day 7 post-implantations. Total RNA was isolated and mRNA expression of Arginase-1, CD206, YM1 and VEGF was measured using RTPCR. CSO, solid bars; control, blank bars. (B) Total protein isolated from day 7 wound mϕ of db/db mice, treated with CSO in vivo, was subjected to capillary electrophoresis immunoassay to measure expression of Arginase 1 protein. (C) Arginase activity of in vivo CSO treated (300 mg) day 7 wound mϕ of db/db mice were measured by Arginase activity assay kit (Colorimetric). (D) mRNA expression of CD74 was measured in day 7 wound mϕ of db/db mice treated with CSO (300 mg). (E) PMA-induced superoxide anion production in day 3 wound mϕ of db/db mice treated in vivo with CSO (300 mg) was measured. For all figure parts, data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3–6); *p < 0.05 compared to wound mϕ treated with equal amounts of white petrolatum (control). (F) Immunocytochemistry (ICC) images of Arginase-1 (red) and NOS2 (red) protein expression in d7 wound mϕ from db/db animals. Day 7 wound mϕ were harvested from PVA sponges coated with CSO (300 mg) implanted subcutaneously. Counter staining was performed using DAPI (nuclear, blue). Scale bar, 20 μm.