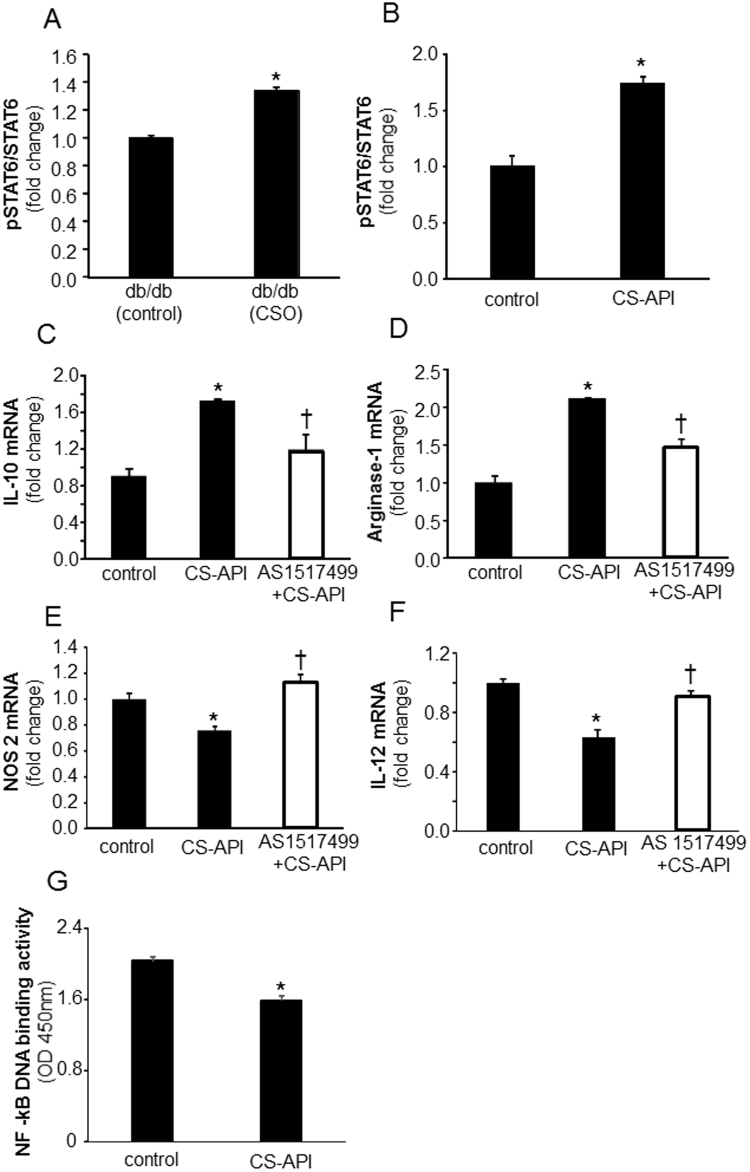
Figure 6.
CS-API activates STAT6 while inhibiting NF-κB pathways in macrophage polarization. (A) Wound mϕ were harvested from PVA sponges coated with CSO (300 mg) implanted subcutaneously in db/db mice on day 7 post-implantations. Phosphorylation of STAT6 was measured using a cell-based ELISA kit. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5); *p < 0.05 compared to white petrolatum (control) treated group. (B) Cultured mouse mϕ were treated with CS-API (250 ng/ml) for 24 hours. Phosphorylation of STAT6 was measured using a cell-based ELISA kit. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5); *p < 0.05 compared to control. (C–F) Cultured mouse mϕ were treated with STAT6 inhibitor AS 1517499 (5 nM) for 1 hour followed by CS-API (250 ng/mL) treatment for 24 hours. mRNA expression of (C) IL-10 (D) Arginase-1 (E) NOS2 and (F) IL-12 was measured. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3–4); *p < 0.05 compared to control, †p < 0.05, compared to CS-API treated group. (G) Cultured mouse mϕ were treated with CS-API (250 ng/ml) for 24 hours. DNA binding activity of LPS (1 µg/ml, 3 h) inducible NF-κB was measured using an ELISA-based (Trans-AM) method. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5); *p < 0.05 compared to control.