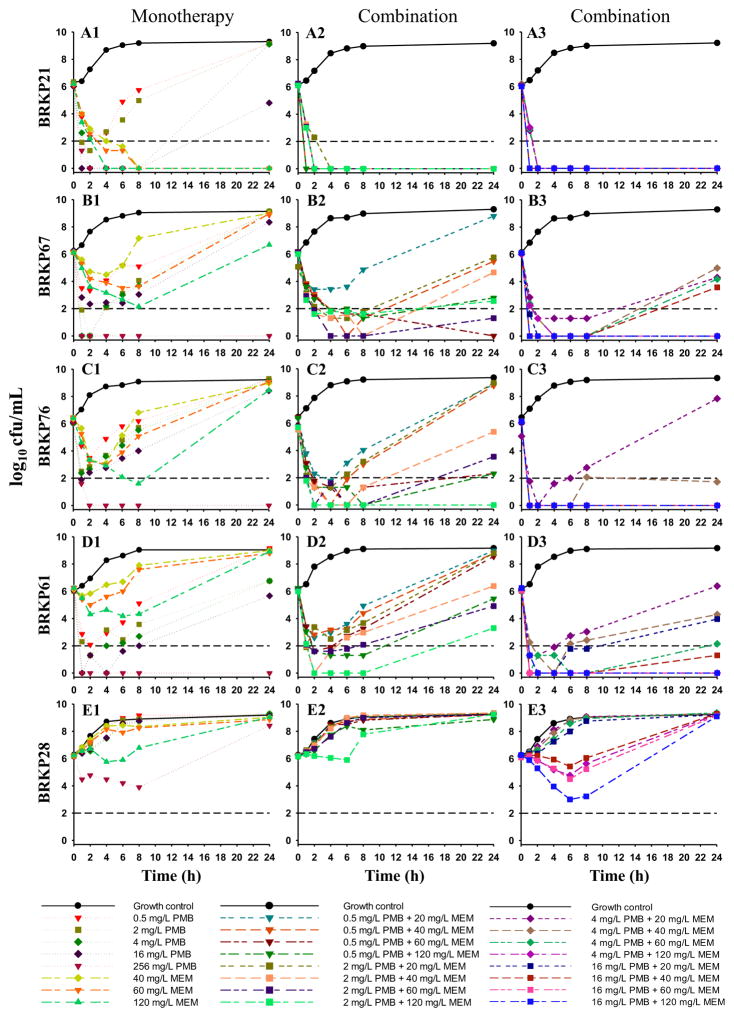
Fig. 1.
Time–kill curves with polymyxin B (PMB) and meropenem (MEM) alone and in combination against an initial inoculum of ca. 106 CFU/mL of PMB-susceptible clinical isolates BRKP21, BRKP61 and BRKP76 and PMB-resistant isolates BRKP67 and BRKP28 over 24 h: PMB (0.5, 2, 4, 16 and 256 mg/L) and MEM (40, 60 and 120 mg/L) as monotherapy (A1–E1, monotherapy); PMB (0.5 mg/L and 2 mg/L) in combination with meropenem (20, 40, 60 and 120 mg/L) (A2–E2, combination); and PMB (4 mg/L and 16 mg/L) in combination with meropenem (20, 40, 60 and 120 mg/L) (A3–E3, combination). Black dashed line represents the limit of quantification for CFU/mL bacterial count.