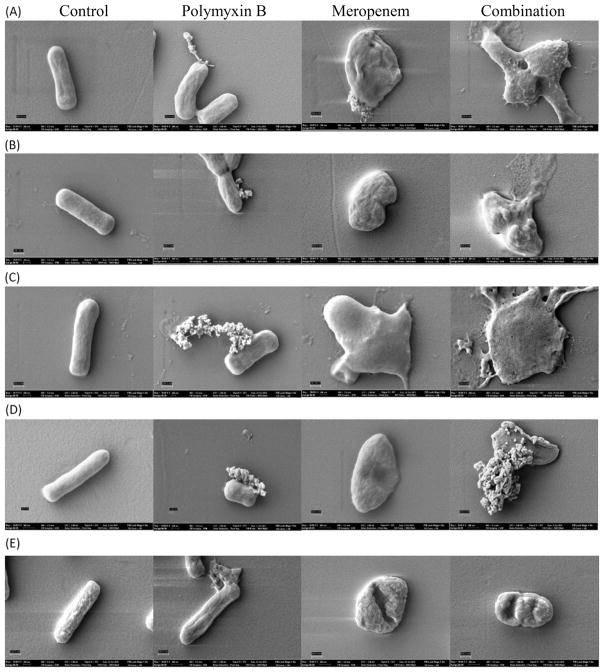
Fig. 3.
Scanning electron microscopy images of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in the absence of treatment (A–E, control) and in the presence of polymyxin B (PMB) alone at 0.5 mg/L (A–E, polymyxin B), meropenem alone at 20 mg/L (A–E, meropenem) and PMB in combination with meropenem (A–E, combination). Magnification at 50,000× with the scale bar set at 300 nm to image individual bacteria of (A) BRKP20 (PMB MIC <0.5 mg/L, meropenem MIC = 16 mg/L); (B) BRKP21 (PMB MIC = 0.5 mg/L, meropenem MIC = 16 mg/L); (C) BRKP27 (PMB MIC = 1 mg/L, meropenem MIC = 16 mg/L); (D) BRKP67 (PMB MIC = 8 mg/L, meropenem MIC = 64 mg/L); and (E) BRKP28 (PMB MIC >128 mg/ L, meropenem MIC = 256 mg/L).