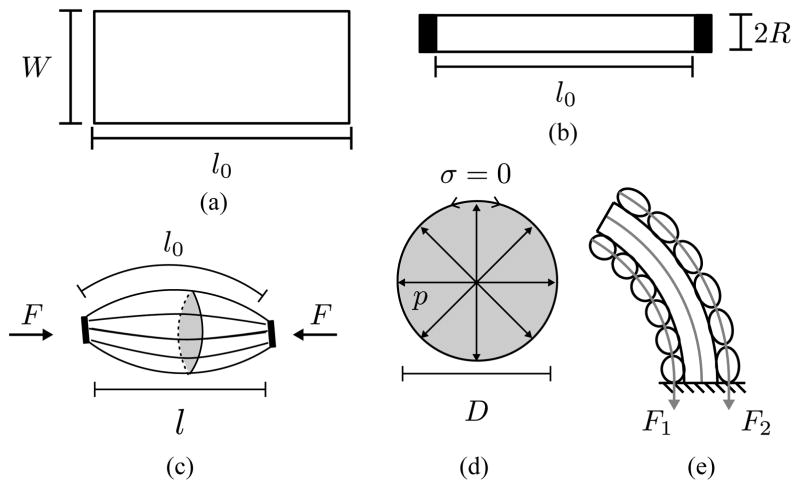
Fig. 4.
(a) A sPAM segment starts as a thin sheet of length l0 and width W, which inflates to a Dtube = 2W/π diameter cylinder. (b) Adding an o-ring to the deflated actuator reduces its width to 2R through wrinkling and folding. (c) When it is inflated, the profile of the actuator bulges between the o-rings, causing it to contract to length l and exert a tension force, F. (d) A parallel circular cross-section of the sPAM, inflated by a pressure, p. It will satisfy zero parallel stress condition (σ = 0) if D < Dtube. (e) sPAMs attached to the pneumatic backbone, exerting forces F1, F2.