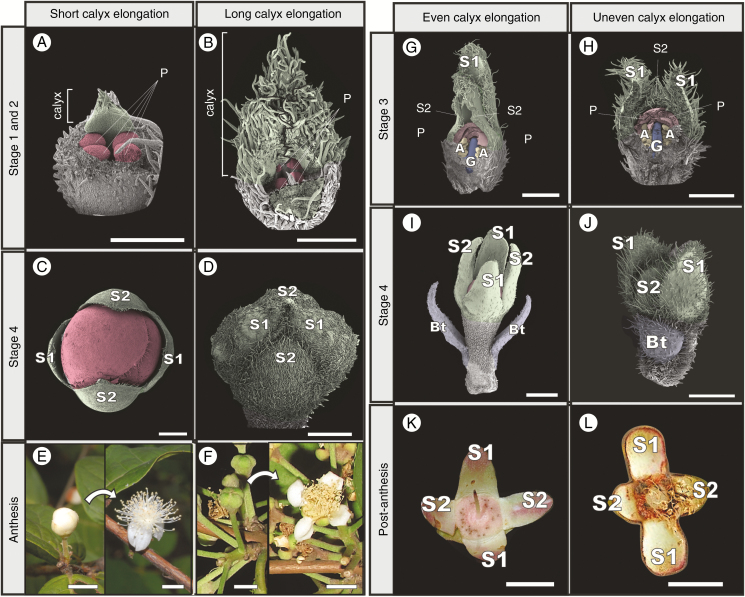
Fig. 5.
Variation of perianth developmental rate in Eugenia. (A) Early development of E. stipitata, showing short calyx contrasting with (B) the extremely elongated calyx of E. acutata. (C) Pre-anthetic stages in E. protenta, showing corolla exposition prior to anthesis. (D) The same stage in E. acutata, showing sepals that cover the whole bud prior to anthesis. (E) Anthesis in E. stipitata, highlighting how exposed the corolla is in the pre-anthetic stage. (F) Anthesis in E. acutata, showing sepals that cover the whole bud prior to anthesis. (G) Stage 3 bud in E. involucrata and (H) E. inversa, showing S1 more developed than S2. (I) Pre-anthetic buds of E. dichroma, with S1 and S2 equally developed, in contrast to the same stage in (J) E. inversa, where S1 is still more developed than S2. (K) Calyx from post-anthetic flower of E. involucrata, showing all sepals the same size in contrast with (L) post-anthetic flower of E. splendens, showing disymmetrical calyx with distinctly larger S1 than S2 sepal pairs. Bt, bracteole; S, sepal; P, petal; A, androecium; G, gynoecium. Scale bars: (A, B) = 250 µm; (C, D, H) = 500 µm; (G, I, J) = 1 mm; (E, F, K, L) = 5 mm. Colour coding in online version: sepals, green; corolla, red; androecium, yellow; gynoecium, blue. Picture in (F) by Augusto Giaretta.