Figure 2. eIF5B Facilitates eIF2-Independent met-tRNAiMet Delivery.
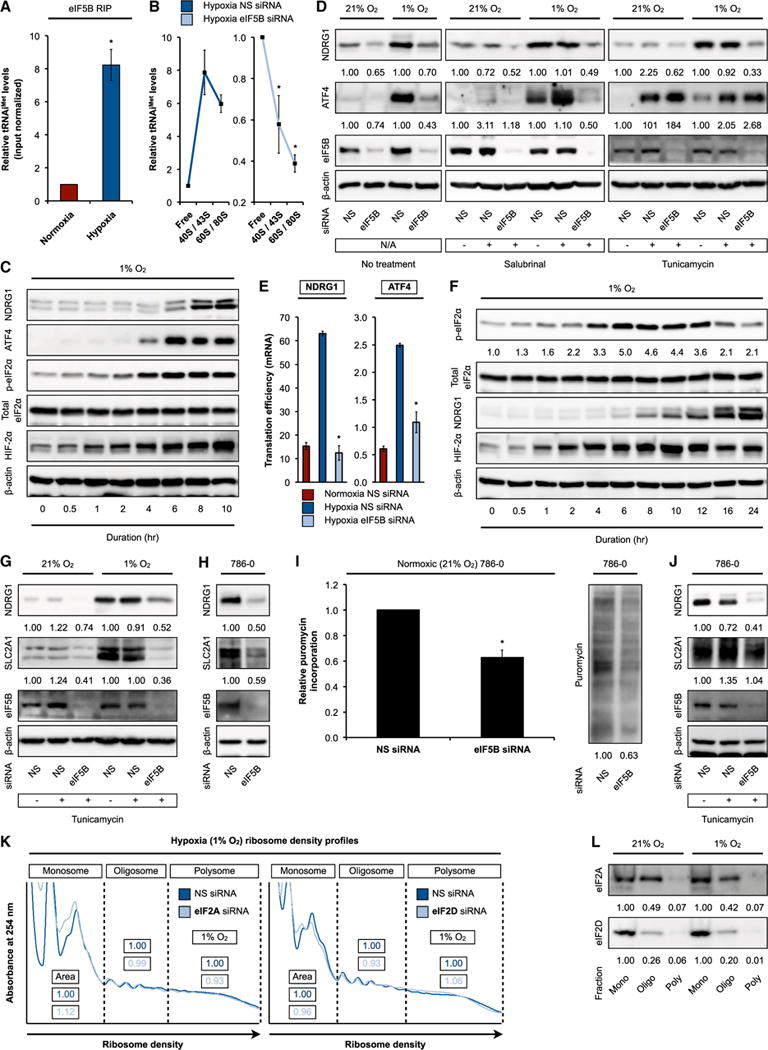
(A) eIF5B RNA immunoprecipitations (RIPs) followed by qRT-PCR measurements of input-normalized tRNAiMet levels from normoxic and hypoxic U87MG.
(B) Normoxic and hypoxic U87MG treated with control non-silencing (NS) or eIF5B-specific siRNA were subjected to ribosome density fractionation, followed by qRT-PCR measurements of tRNAiMet levels in the indicated fractions. (C and D) Representative immunoblots of hypoxic U87MG (C) and normoxic and hypoxic (1% O2, 10 hr) U87MG (D) treated with NS or eIF5B-specific siRNA (left panel) and with salubrinal (middle panel) or tunicamycin (right panel).
(E) Normoxic and hypoxic U87MG treated with NS or eIF5B-specific siRNA were subjected to ribosome density fractionation, followed by mRNA level measurements by qRT-PCR. Translation efficiency was defined as the ratio of polysome to monosome abundance.
(F–H) Representative immunoblots of hypoxic U87MG (F), normoxic and hypoxic U87MG treated with NS or eIF5B-specific siRNA and tunicamycin (G), and normoxic 786-0 treated with NS or eIF5B-specific siRNA (H).
(I) Puromycin incorporation measurements (left panel) and representative immunoblot (right panel) in normoxic 786-0 treated with NS or eIF5B-specific siRNA.
(J) Representative immunoblots of normoxic 786-0 treated with NS or eIF5B-specific siRNA and tunicamycin.
(K) Ribosome density profiling of hypoxic U87MG treated with NS, eIF2A-specific (left panel), or eIF2D-specific (right panel) siRNA. Area under curve measurements (area) are shown.
(L) Representative immunoblots of normoxic and hypoxic U87MG subjected to ribosome density fractionation.
Mono, monosome (40/60/80S); oligo, oligosome; poly, polysome. Error bars represent SEM. *p < 0.05. See also Figure S2.
