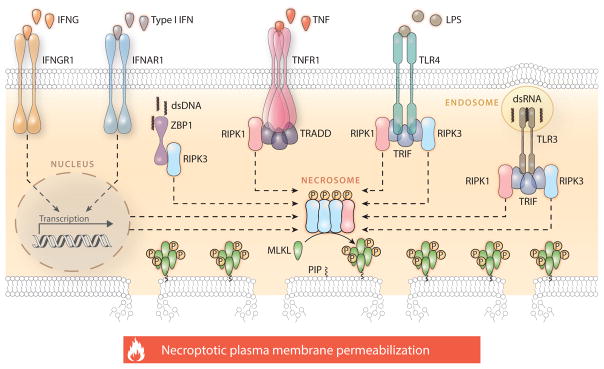
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis. Necroptosis critically depends on the receptor-interacting serine-threonine protein kinase 3 (RIPK3)–mediated phosphorylation of mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL), resulting in MLKL oligomerization, translocation to the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane, and cell death. The formation of the RIPK3- and MLKL-containing complex that precipitates necroptosis, the so-called necrosome, can be elicited by extracellular signals (such as the ligation of death receptors) as well as by intracellular cues (such as the presence of viral nucleic acids) and is regulated by a complex network of physical and functional protein-to-protein interactions. The best characterized signal transduction cascade resulting in necroptotic cell death is initiated by TNFR1 (official name: TNFRSF1A, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A) ligation in the presence of caspase inhibitors and/or SMAC (official name: DIABLO, diablo IAP-binding mitochondrial protein) mimetics and critically depends on the phosphorylation of RIPK3 by RIPK1. In several other circumstances, however, RIPK1 is dispensable for necroptotic responses or even inhibits them in an active manner. This applies to various other TNFR1 interactors that participate in necroptotic signaling, most of which also regulate caspase 8 (CASP8)-dependent apoptosis and proinflammatory NF-κB activation. Please note that several physical or functional interactions have been omitted for the sake of simplicity. Abbreviations: dsDNA, double-stranded DNA; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; IFN, interferon; IFNAR1, interferon (alpha and beta) receptor 1; IFNG, interferon gamma; IFNGR1, interferon gamma receptor 1; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; P, phosphate; PIP, phosphatidylinositol phosphate; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRADD, TNFRSF1A associated via death domain; TRIF (official name TICAM1), toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 1; ZBP1, Z-DNA binding protein 1.