Figure 9.
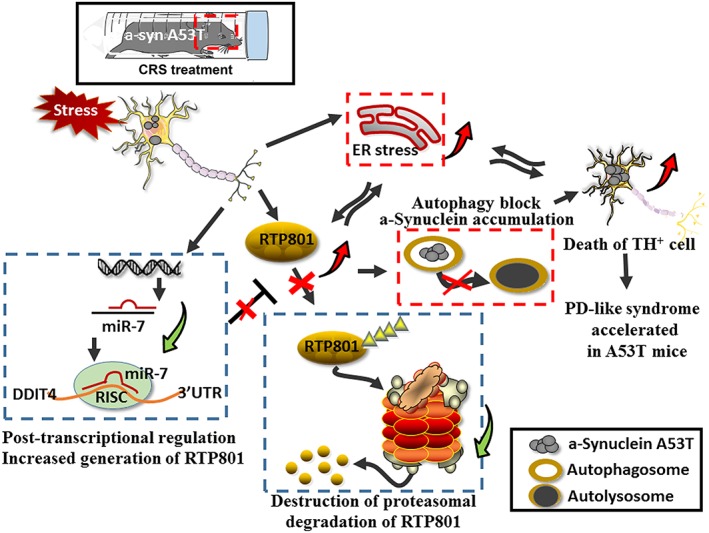
Schematic summary of the results. CRS treatment induced RTP801 up‐regulation and caused neurodegeneration, or even death, of TH+ cells in A53T mice. PD‐like pathogenesis was mediated by the robust enhancement of RTP801. Increased content of RTP801 occurred via inhibition of miR‐7, which post‐transcriptionally inhibited RTP801 expression and retarded proteasomal degradation. Up‐regulation of RTP801 intensified the toxicity of αSyn A53T for dopaminergic neurons. The crosstalk between ER stress and up‐regulated RTP801 reinforced the extra stress exposure. The block of autophagy that increased accumulation of oligomeric forms of αSyn aggravated the pathogenesis.
