Figure 3.
Blinded validation of the HLA-A*02:01 library by neoantigen-specific TCRs.
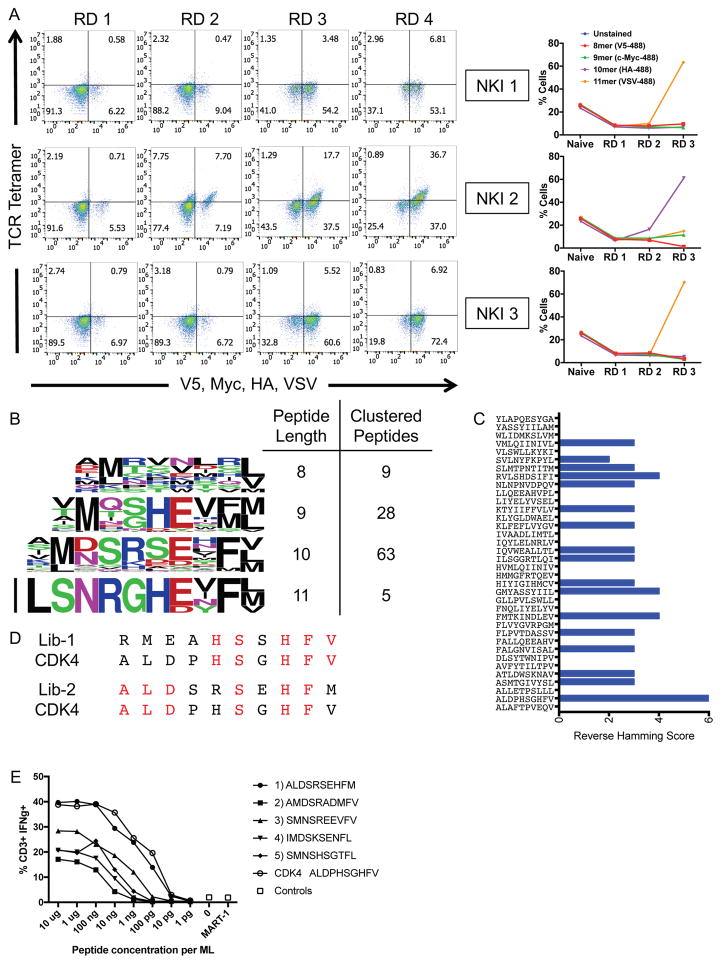
(A) Three TCRs of blinded specificity separately enrich the HLA-A*02:01 library for a specific peptide length according to epitope tag staining over the rounds of selection. The left panels indicate tetramer and epitope staining after all 4 rounds of selection have completed and the right panels indicate epitope staining through the course of selections.
(B) Unique peptides selected by NKI 2 in round 3 of the selection are parsed by peptide length and clustered by reverse hamming distance. The number of peptides identified in the cluster are shown on the right along with the respective peptide lengths.
(C) The maximum reverse hamming distance computed between every 10mer of the selected peptides by NKI 2 at round 3 and each 10mer neoantigen peptide from the list of 127 total neoantigens.
(D) Two peptides Lib-1 and Lib-2 from the selected library closely resemble the 10mer neoantigen peptide ALDPHSGHFV derived from CDK4. Identical amino acids with the neoantigen are colored in red.
(E) The top 5 peptides of length 10 selected by the NKI 2 TCR were used to stimulate peripheral blood lymphocytes transduced with NKI2 TCR, which is specific for the CDK4 neoantigen ALDPHSGHFV. Transduced lymphocytes were mixed 1:1 with JY cells pulsed with peptide, control peptide, or no peptide, and IFNγ production as measured by intracellular antibody staining was assessed using flow cytometry.
Related to Table S2.