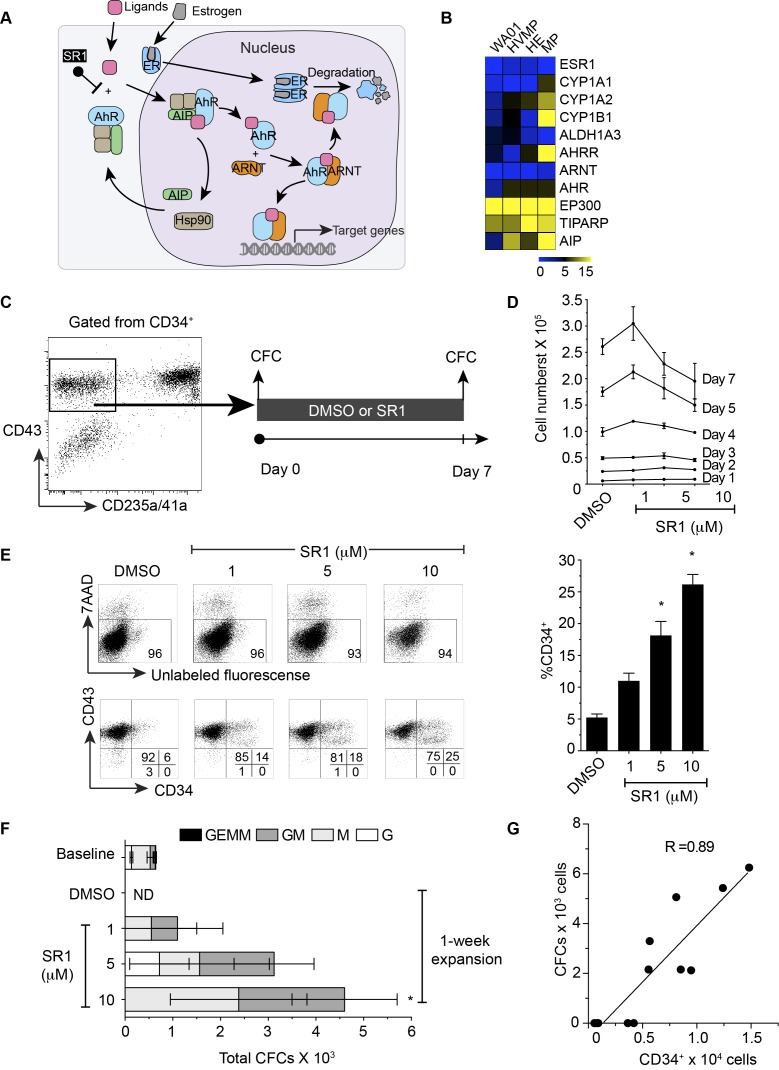
Figure 1.
Aryl hydrocarbon signaling and its effects on multipotent hematopoietic progenitor cells. (A) Schematic diagram showing current mechanisms of AHR regulation. (B) Heat map showing the expression of genes associated with AHR signaling and estrogen receptor in WA01, HVMP, HE, and MP. (C) Schematic diagram showing the experimental outline. FACS-sorted live CD235a/41a-CD34+CD43+ cells from day 8 WA01/OP9 coculture shown in the gate were cultured in the presence or absence of SR1 for 7 days. The sorted cells (day 0) and expanded cells (day 7) were plated in methylcellulose for the colony-forming cell (CFC) assay. (D) Cross-sectional presentation of total viable cell numbers on a day-to-day basis. * indicates significant difference compared with DMSO. (E) Representative flow cytometric dot plots showing the effect of SR1 on cell viability after 7-day expansion using 7AAD (upper panel) and CD43 vs CD34 expression on the expanded cells (lower panel). Right bar graph summarizes a percentage of CD34 expression shown in the dot plots. (F) Absolute number of colony-forming cells in WA01-derived MPs (baseline, day 0), expanded cells with DMSO only, and expanded cells with 1, 5 and 10 µM SR1 (G) Correlation between colony-forming cells and CD34 expression. Error bars represent SEM from 3 experiments. * indicates p < 0.05 compared to DMSO. HVMP = hematovascular mesodermal precursor, HE = hemogenic endothelium, MP = multipotent hematopoietic progenitor, ER = estrogen receptor, AHR = aryl hydrocarbon receptor, AIP = AHR interacting protein, ARNT = AHR nuclear translocator, Hsp90 = heat shock protein 90, SR1 = StemRegenin 1, ND = not detectable