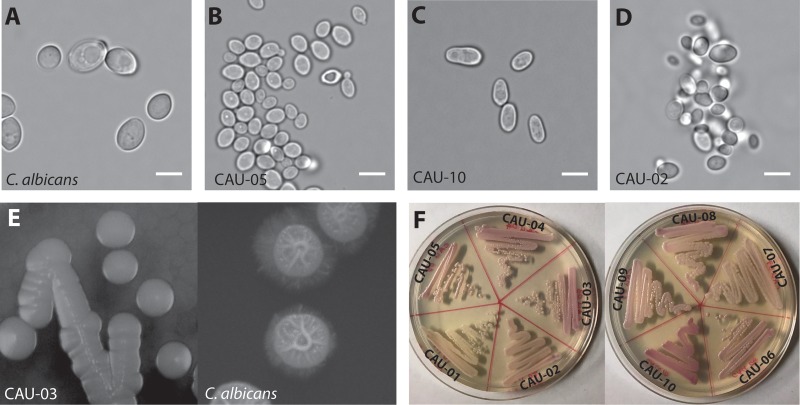
FIG 1.
Basic morphology of the C. auris clinical isolates used in this study. (A to D) Micrographs of C. albicans SC5314, consisting of large ovoid cells (A), C. auris strains consisting of spherical to ovoid cells (CAU-05 shown) (B) or ellipsoidal cells (CAU-10 shown) (C), and some highly aggregative strains (CAU-02 shown) (D). (E) Colony morphology of C. auris (CAU-03 shown). C. auris forms smooth, unwrinkled colonies on Spider medium plates after 7 days of incubation at 37°C, while C. albicans SC5314 forms rough colonies. (F) C. auris strains form smooth, light- to dark-pink circular colonies on CHROMagar plates after incubation for 48 h at 37°C. Bars, 5 μm.