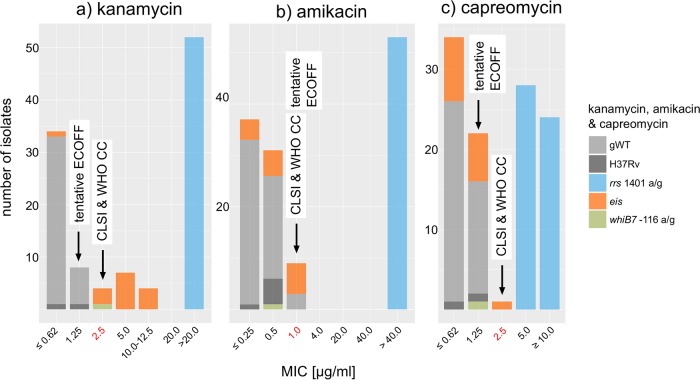
FIG 5.
MIC distributions for kanamycin, amikacin, and capreomycin. The direct alteration of rrs, the shared target of kanamycin, amikacin, and capreomycin, via the A1401G mutation is known to confer unequivocal cross-resistance to all three drugs, which was in agreement with the pooled MIC data (60). In contrast, the current CCs for kanamycin were found to truncate the MIC distribution for isolates with eis and whiB7 mutations (27). This meant that isolates with a MIC of 2.5 μg/ml were misclassified as susceptible despite the fact that these included mutations had been shown to result in elevated MICs using allelic exchange experiments (i.e., eis −37 g/t, eis −10 g/a, and whiB7 −116 a/g) (25, 26). In contrast, neither eis nor whiB7 mutations had a significant impact on the MICs of amikacin or capreomycin (based on previous data, the fact that the tentative ECOFF for capreomycin for our study was below the critical concentration was likely an artifact due to the small number of gWT isolates included in this study) (61).