Figure 5.
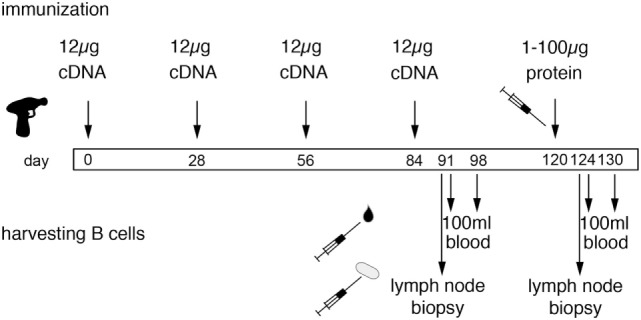
Schematic diagram of the genetic immunization strategy to generate nanobodies (Nbs) against membrane proteins. The scheme illustrates time points for immunization and harvesting of blood cells in order to obtain Nbs directed against membrane proteins in native conformation. Each cDNA immunization comprises 12 shots, each with 1 µg plasmid DNA coated onto 1 mg of gold particles (see Figure 4). Boost immunizations are spaced 3–4 weeks apart. A final protein boost is performed with the purified ecto-domain, cells transfected with the membrane protein of interest, or protein immunoprecipitated from transfected cells with bead-conjugated antibodies. B cells are harvested from a sample of blood and/or a lymph node biopsy 7 days after the last cDNA boost and 4 days after the last protein boost, i.e., at the peak of lymph node swelling. A second sample of blood is drawn 6–7 days thereafter. i.e., at the estimated peak of migration of expanded B cells from the lymph node to the bone marrow. We have selected antigen-specific Nbs from libraries constructed from lymphocytes obtained both before and after the protein boost. In case of similar Nbs obtained from both samplings, it can be inferred that the respective clone was induced by DNA immunization—and that this clone was probably reactivated by the final protein boost.
