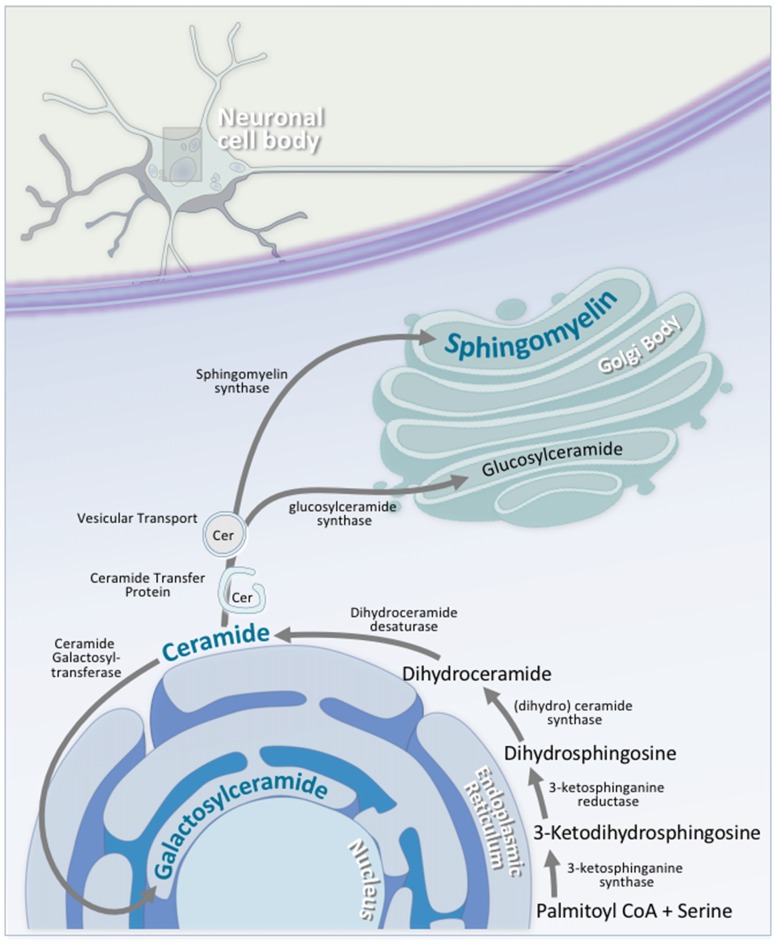
Figure 5.
Neuronal sphingolipid synthesis takes place across multiple cellular compartments. Sphingolipid synthesis begins at the cytosolic leaflet of the ER. Via a series of reactions, palmitoyl CoA and serine are converted to ceramide. A portion of this ceramide is transported to the luminal leaflet of the ER, where ceramide galactosyltransferase (CGT) converts the ceramide to galactosylceramide; an essential neuronal sphingolipid. Another portion of this ceramide is transported to the Golgi complex, where it is converted to either glucosylceramide on the cytosolic side of the Golgi via glucosylceramide synthase, or to sphingomyelin on the luminal side by sphingomyelin synthase. Transport of ceramide from the ER to the Golgi complex is facilitated by either ceramide transfer protein (CERT) or vesicular transport.