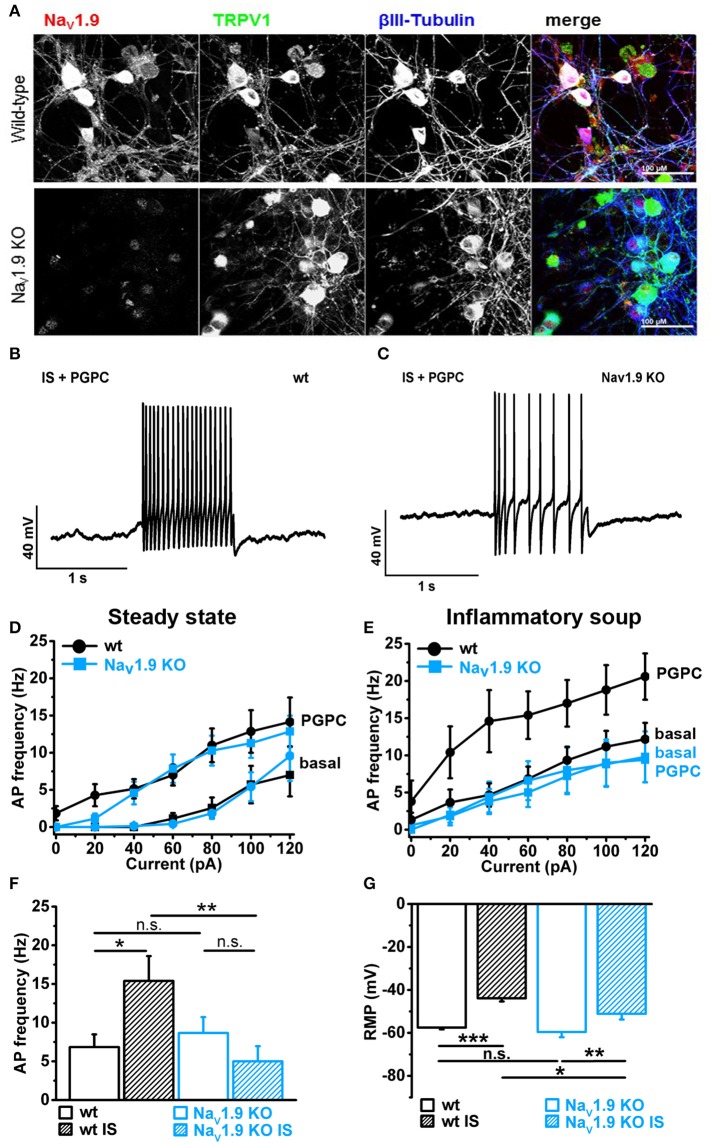
Figure 5.
Inflammatory mediators recruit NaV1.9 to potentiate OxPL function. (A) Indirect immunofluorescent staining of 48 h old primary DRG cultures from Bl6 wt mice or NaV1.9 KO mice were stained against NaV1.9 (red), TRPV1 (green) and βIII-Tubulin (blue). (B) Representative train of action potentials, recorded from a murine DRG neuron in response to a 1 s current injection of 80 pA after incubation in IS for 30 min and application of 30 μM PGPC. (C) Representative train of action potentials from a murine NaV1.9 KO DRG neuron in response to a 1 s current injection of 80 pA after incubation in IS for 30 min and application of 30 μM PGPC. (D) Frequency of action potential firing of wild-type and NaV1.9 KO neurons in response to variable current injections ranging from 0 to120 pA before (Basal) and after stimulation with 30 μM PGPC under steady state conditions (mean ± SEM; n = 7 from 6 mice; statistics see Table 3). (E) Action potential frequencies of wild-type and NaV1.9 KO DRG in response to variable current injections before (Basal) and after application of 30 μM PGPC and pretreatment with inflammatory soup [n = 5 from 5 mice (wild-type); n = 5 from 3 mice (NaV1.9 KO); mean ± SEM; statistics see Table 3]. (F) Frequency of action potentials obtained after PGPC application during 60 pA current injections for 1 s from wild-type and NaV1.9 KO DRG neurons without (open bars) or with (striped bars) pretreatment of cells with inflammatory soup (IS) [n = 5–7 of 3 mice; mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA; post-hoc Holm-Sidak; F(3, 21) = 3.86; *p = 0.014; **p = 0.0054]. (G) Resting membrane potential (RMP) of wild-type and NaV1.9 KO DRG neurons obtained under either steady state conditions (wt: n = 19; NaV1.9 KO: n = 12) or after pretreatment with inflammatory soup [wt: n = 8; NaV1.9 KO n = 9; mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA; post-hoc Holm-Sidak; F(3, 46) = 13.34; *p < 0.019; **p = 0.0029; ***p = 3.95E-06].