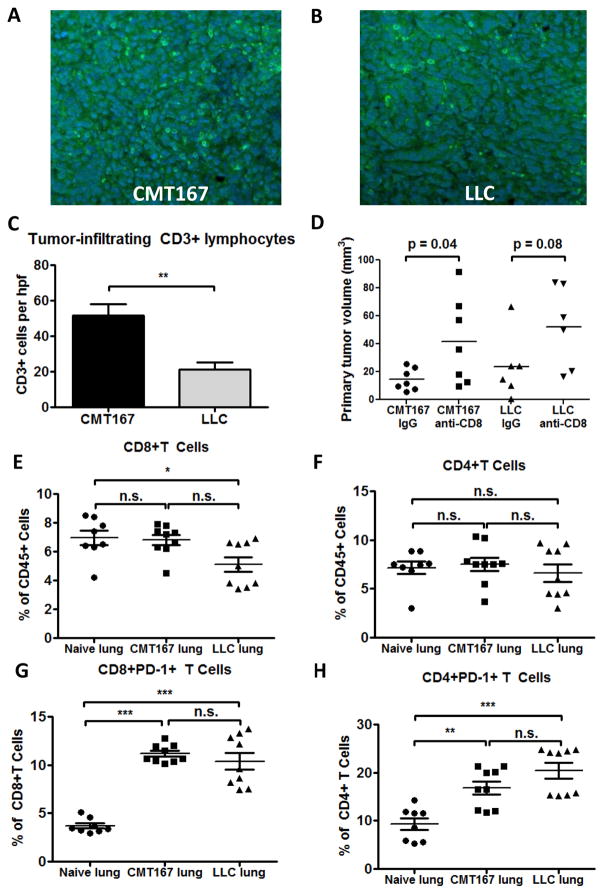
Fig. 5.
Both CMT167 orthotopic lung tumors and LLC orthotopic lung tumors generate an adaptive immune response and induce PD-1 expression on T cells. Tissue sections from CMT167 (representative image shown in Fig. 5A) and LLC (representative image shown in Fig. 5B) tumor-bearing mice were stained for CD3 (FITC, green) and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Magnification x20. (C) Quantification of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in CMT167 tumors (n = 9) and LLC tumors (n = 6). (D) Effects of CD8+ T cell immunodepletion on growth of CMT167 (n = 7 each group) and LLC orthotopic tumors (n = 6 each group). CMT167 (n = 9, same mice as in Fig. 3B–F) or LLC tumor-bearing lungs (n = 9) were analyzed by flow cytometry and compared with lungs from naive mice (n = 8) for (E) CD8+ T cells, (F) CD4+ T cells, (G) PD-1 expression on CD8+ T cells, and (H) PD-1 expression on CD4+ T cells. Statistically significant differences are indicated as determined by Student unpaired t test (C-D) or by one-way ANOVA (E-H); * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01, *** = P < 0.001.