Figure 1. 5/6Nx induces progressive renal pathology.
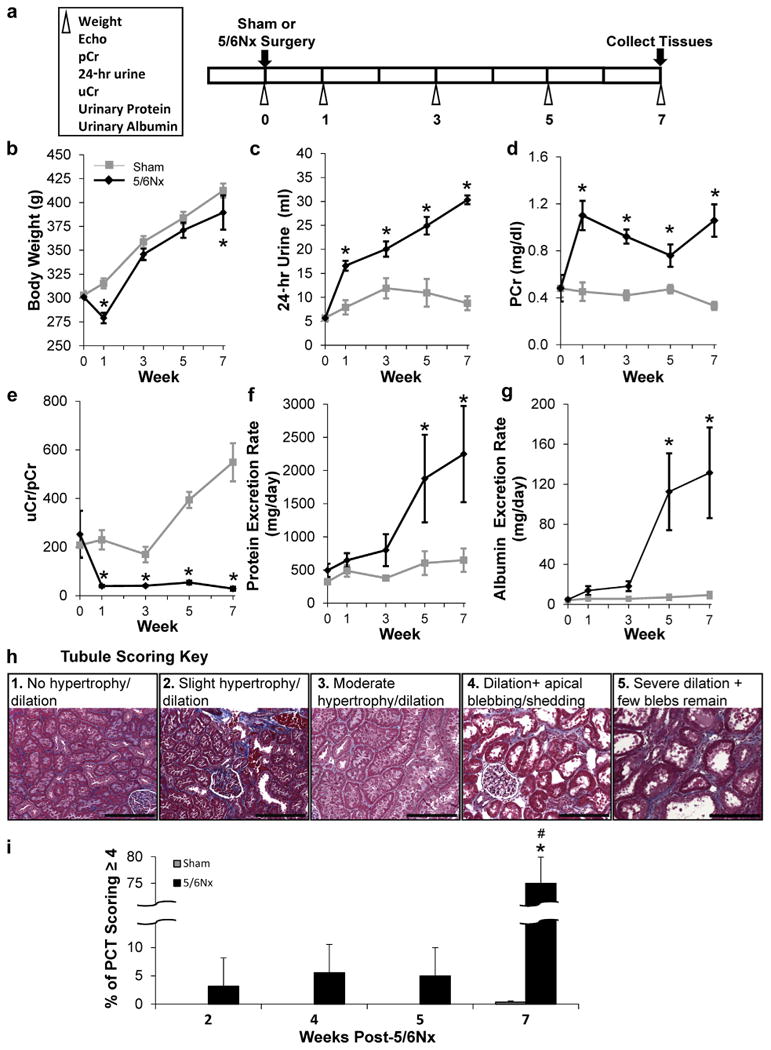
Phenotyping protocol used (a). (b) Repeated phenotypic measurements of body weight and indices of impaired renal function with 5/6Nx including increased 24-hour urine volume (c), increased plasma creatinine levels (d), a reduced urinary to plasma creatinine ratio (uCr/pCr) (e), progressively increasing protein (f), and albumin excretion rates (g). N = 5–6 per group; *P< 0.05 versus sham controls; 2-way repeated-measures analysis of variance. Renal pathology was evaluated in animals used for LV gene expression analysis at weeks 2, 4, 5, and 7 post-5/6Nx. Proximal tubular damage including pronounced dilation, apical blebbing, and loss of brush border (damage score of 4–5) was extensive 7 weeks after 5/6Nx surgery and not at early time points studied. Tubular scoring key (h). Weeks post-5/6NX (i). N = 5–6 per group; *P < 0.05 versus sham controls; #P < 0.05 versus 5/6Nx at 2, 4, and 5 weeks; 2-way analysis of variance. 5/6Nx, 5/6 nephrectomy; Echo, echocardiogram; PCT, proximal convoluted tubules. Bar = 200 μm. To optimize viewing of this image, please see the online version of this article at www.kidney-international.org.
