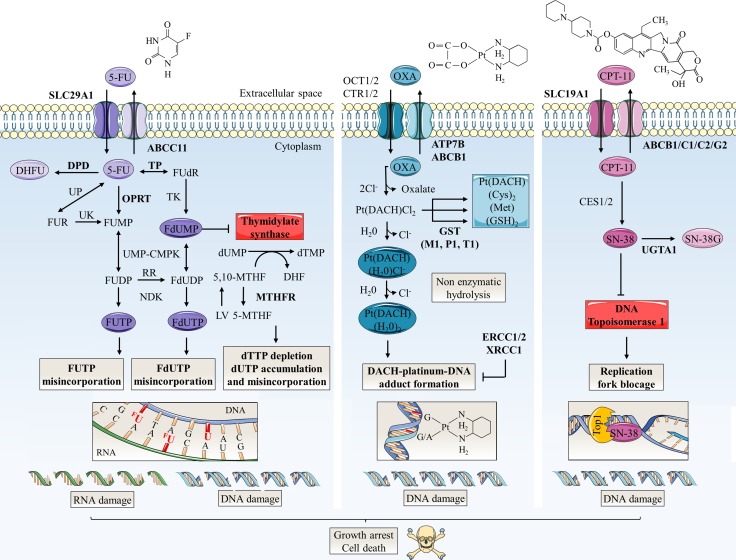
Figure 3. Schematic representation of mechanisms of action and resistance biomarkers in main colorectal cancer chemotherapies.
5-FU, oxaliplatin (OXA) and CPT-11 are the principal anti-colorectal cancer drugs. Arrow-headed lines indicate metabolite chemical conversion whereas bar-headed lines represent inhibition of chemical process (OXA pathway) or enzymes (5-FU and CPT-11 pathways). The anabolic pathways are dark-colored and the catabolic pathways are light-colored. Some of therapy resistance biomarkers are indicated in bold. 5-FU penetrates in tumor cell by nucleoside solute carrier (SLC) transporters such as SLC29A1. Then, 5-FU is converted to three main active metabolites: FdUMP, fluorodeoxyuridine triphosphate (FdUTP) and fluorouridine triphosphate (FUTP) which acts as antimetabolites and pyrimidine analogues. FdUMP decreases the biosynthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides by inhibiting TS, the enzyme that catalyzes the rate limiting step in DNA synthesis by catalysing the reductive methylation of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP) using 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (5,10-MTHF) as the methyl donor. By this way, FdUMP inhibits DNA synthesis and repair leading to DNA strand breakage and cell death notably by induction of apoptosis. 5-FU is also incorporated into DNA (via FdUTP) or RNA (via FUTP), leading to other cytotoxic actions including DNA fragmentation and decrease in protein synthesis. LV expands the intracellular pool of 5,10-MTHF and increases the toxicity of 5-FU. DPD mediates the conversion of 5-FU to non-active dihydrofluorouracil (DHFU). 5-FU catabolism also includes efflux of metabolites by ABC transporters such as ABCC11. TS and OPRT over-expressions are major molecular mechanism of 5-FU resistance. OXA, a third generation of alkylating platinum agent, is transported mainly by organic cation (OCT1/2) and copper (CTR1/2) transporters. On the contrary, P-type ATPase (ATP7A/B) transporters and ABC transporters promote its efflux. Inside the cell, displacement of the labile oxalate and non-enzymatic hydrolysis promotes the conversion of OXA in active metabolites such as monoaquo-1,2-diaminocyclohexane (DACH) platinum and diaquo-DACH platinum. These products alkylate DNA leading to G/G or G/A intra-strand crosslinks which, if not repaired, will block both DNA replication and transcription leading to apoptosis. Hydrophobicity and bulkiness of the DACH ring prevents the MMR proteins from binding to OXA. Excision repair cross-complementation 1 and 2 (ERCC1/2) and X-ray repair cross complementing 1 (XRCC1) are involved in repair of DNA adducts. Cellular detoxification processes include metabolites targeting for excretion by conjugation of aquated compounds to cysteine (Cys), methionine (Met) or GSH. In particular, conjugation of GSH is catalysed by GST (-mu GSTM1, -pi GSTP1 and -theta GSTT1). CPT-11 is transported by SLC transporters such as SLC19A1. Inside the cell, CPT-11 is converted into the active SN-38 by carboxylesterases 1 and 2 (CES1/2). SN-38 binds and stabilizes its target DNA Top1 responsible for supercoiled DNA relaxation during replication and transcription. SN-38 inhibits the relegation step and the collision of the SN-38/Top1 complex with the moving DNA replication fork leads to irreversible arrest of the replication fork and double DNA stranded breaks. This damage causes cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. CPT-11 resistance mechanisms include SN-38 glucuronidation in inactive SN-38 glucuronide (SN-38G) by uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1 polypeptide A1 (UGT1A1) and overexpression of ABC transmembrane transporters (ABCB1, ABCC1, ABCC2 and ABCG2) responsible for efflux of SN-38. 5-MTHF: 5-methyltetrahydrofolate; Cl-: chlorine; DHF: dihydrofolate; dTTP: deoxythymidine triphosphate; dUTP: deoxyuridine triphosphate; FdUDP: fluorodeoxyuridine diphosphate; FU: fluorouracil; FUDP: fluorouridine diphosphate; FUMP: fluorouridine monophosphate; FUR: fluorouridine; MTHFR: methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase; NDK: nucleoside-diphosphate kinase; Pt(DACH)(Cl2): dichloro-DACH platinum; Pt(DACH)(H20)2: diaquo-DACH platinum; Pt(DACH)(H20)Cl-: monoaquo-DACH platinum; RR: ribonucleotide reductase; UK: uridine kinase; UMP-CMPK: uridine monophosphate/cytidine monophosphate kinase; UP: uridine phosphorylase.