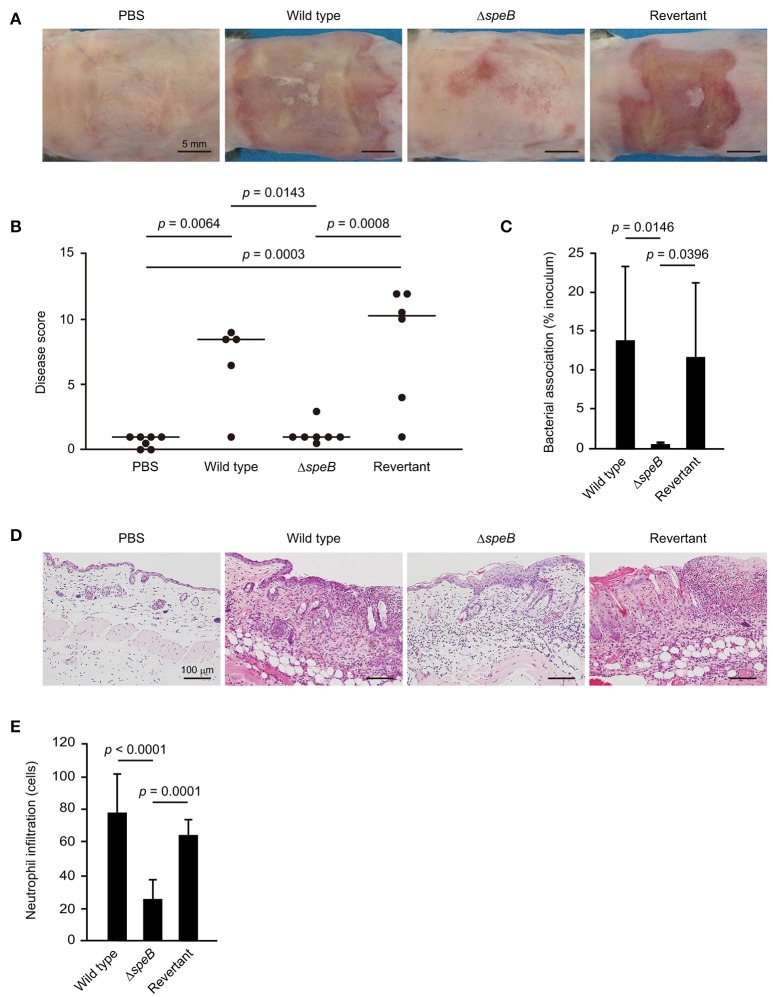
Figure 3.
SpeB is critical for the development of cutaneous lesions. Mice were infected in an epicutaneous manner with strain 591, the speB deletion mutant, or the revertant strain for 3 days. (A) Representative gross appearance of mouse skin samples after infection with the S. pyogenes strains. (B) Cutaneous disease score was determined as the sum of individual scores for erythema, edema, erosion, and purulence, graded as follows: 0 (none), 1 (mild), 2 (moderate), and 3 (severe). The median value for each group is shown as a horizontal bar. (C) Each cutaneous tissue homogenate was serially diluted and plated on a THY agar plate containing 5% sheep blood. Data shown represent the mean ± S.D. of quintuplet samples and are representative of at least three independent experiments. (D) Cutaneous tissues from infection sites were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Data shown are representative of at least three separate experiments. (E) Cutaneous inflammation was evaluated based on neutrophil infiltration into the epidermis and dermis. Data were obtained from five random fields of view (x400) and are presented as the mean ± S.D. of 9 independent samples. Statistically significant differences were evaluated using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test.