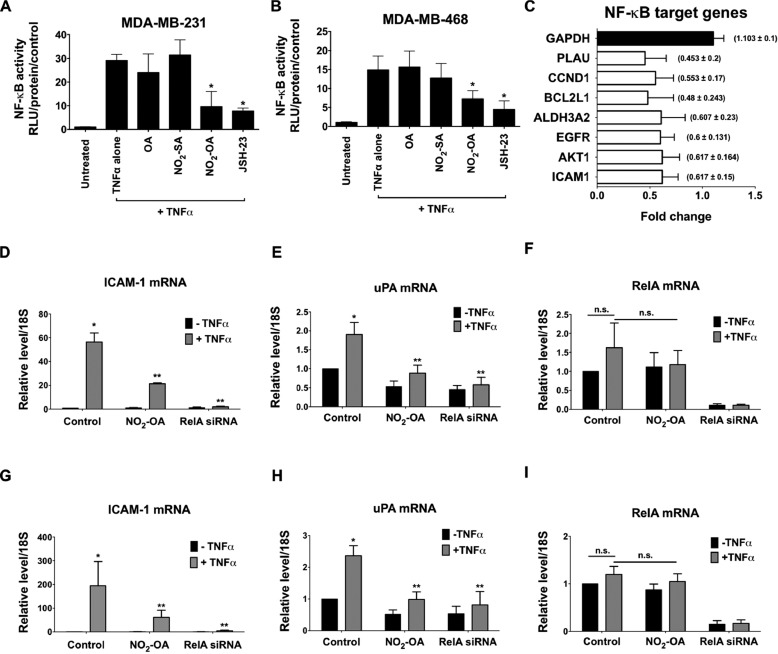
Figure 6.
NO2-OA inhibits TNFα-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity in TNBC cells. The effect of NO2-OA on TNFα-induced activation of NF-κB–dependent reporter gene transcription was measured in NF-κB-luciferase reporter–transfected MDA-MB-231 (A) or MDA-MB-468 (B) cells. *, p < 0.05 versus TNFα alone (n = 3). Significance was determined by Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's post test with Bonferroni corrections for multiple comparisons. C, determination of NF-κB target genes down-regulated by NO2-OA in MDA-MB-468 cells using a human NF-κB target PCR array. Histograms represent the fraction of mRNA expression in NO2-OA–treated versus untreated cells. GAPDH was used as an internal control (black bar). Shown is the effect of NO2-OA on expression of ICAM-1 (D), uPA (E), or RelA (F) genes in TNFα-induced MDA-MB-231 cells. Similarly, the effect of NO2-OA on expression of ICAM-1 (G), uPA (H), or RelA (I) genes in TNFα-induced MDA-MB-468 cells is shown. The -fold increase relative to untreated controls is presented. *, p < 0.05 versus untreated control; **, p < 0.05 versus TNFα alone. n.s., not significant. Significance was determined by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey post test. All data are presented as mean ± S.D. (error bars) (n = 5).