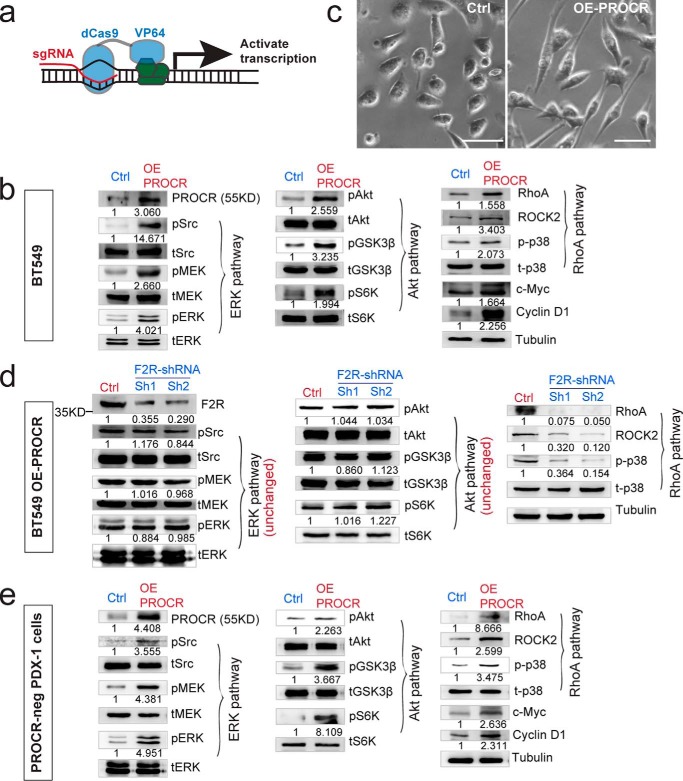
Figure 4.
F2R mediates the activation of RhoA pathway by PROCR, not the activation of ERK and PI3K–Akt–mTOR pathways. a, illustration of activating endogenous PROCR expression using CRISPR interference system, through viral infection with dCas9-VP64 and sgPROCR. b, Western blot indicating that ERK, PI3K–Akt–mTOR, and RhoA–ROCK signaling activities are all up-regulated as a consequence of PROCR overexpression in BT549 cells using the system in (a), including increased c-Myc and cyclin D1 levels. c, overexpression of PROCR in BT549 cells induces change of cell shape as visualized by phase contrast. Scale bars represent 20 μm. d, Western blot showing that in BT549 cells with PROCR overexpression, knockdown of F2R by two independent shRNAs (Sh1 or Sh2) attenuates F2R level and RhoA–ROCK signaling, whereas it is ineffective to ERK and PI3K–Akt–mTOR pathways. e, Western blot indicating that ERK, PI3K–Akt–mTOR, and RhoA–ROCK signaling activities are all up-regulated in isolated PROCR-neg PDX-1 cells as a consequence of PROCR overexpression, including increased c-Myc and cyclin D1 levels. Western blots in the same panel are from the same batch of cells using the same loadings, thus only one loading control is shown at the end of the panel. For a better illustration, they are shown as three separated columns representing ERK, Akt, and RhoA pathways, respectively. Each experiment was repeated three times or more.