Fig. 1.
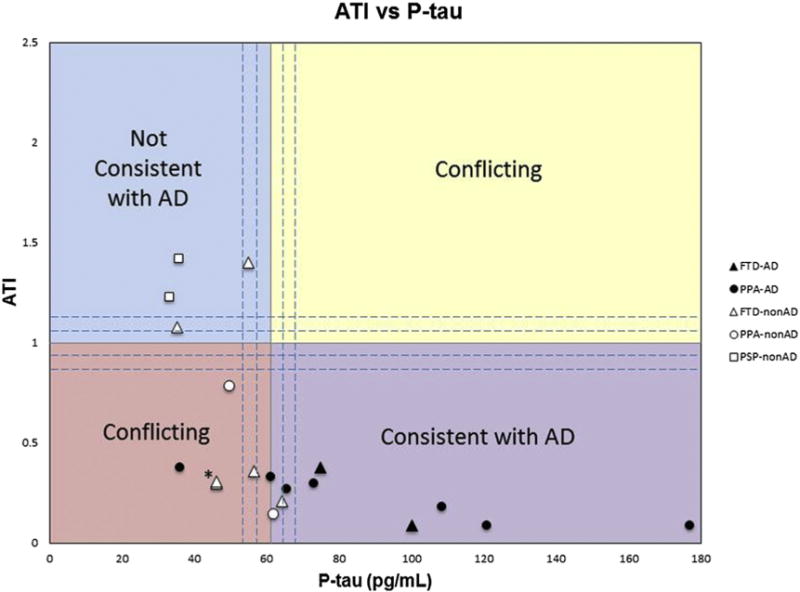
The amyloid-tau index (ATI) versus phosphorylated-tau (p-tau) in picograms per milliliter for all patients with nonamnestic dementia syndromes and autopsy-confirmed pathologies. The upper left quadrant contains values not consistent with AD, whereas the lower right quadrant represents values consistent with AD. The upper right and lower left quadrants represent values with conflicting information. The dashed lines surround the regions considered to lie within a borderline zone and are bound by ATI ranging from 0.8 to 1.2 and p-tau of 54 to 68 pg/mL. Black symbols represent AD pathology and white symbols represent nonAD pathology. Triangles denote FTD as clinical diagnosis, circles denote PPA as the clinical diagnosis, and squares denote PSP as a clinical diagnosis. Abbreviations: AD, Alzheimer’s disease; FTD, frontotemporal dementia; PPA, primary progressive aphasia; PSP, progressive supranuclear palsy. *Note these are two data points that are very close together, both are white triangles representing FTD-nonAD.
