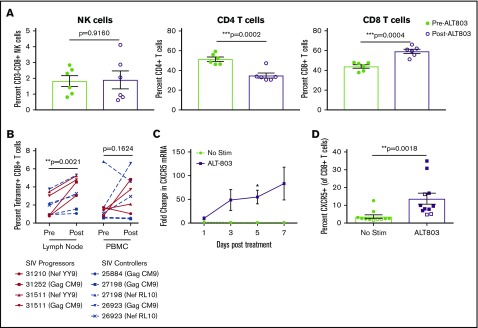
Figure 3.
ALT-803 drives SIV-specific CD8+T cells to lymph nodes in vivo and triggers upregulation of CXCR5 in vitro. SIV-infected RMs received 100 μg/kg of ALT-803. Lymph nodes were sampled before ALT-803 treatment and 5 days posttreatment. (A) The percentage of CD3-CD8+ NK cells, CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells were determined in single-cell suspensions derived from AxLN before and after treatment with 100 μg/kg ALT-803. (B) Percent of SIV-specific CD8+ T cells as measured by MHC class I tetramer staining in lymph nodes and PBMCs. Animal identification numbers and MHC-I tetramer used are indicated. SIV progressors (n = 3) are indicated by solid red lines, and SIV controllers (n = 3) are indicated by dashed blue lines. (C) CD8β-sorted T cells from 6 RMs were cultured in vitro for 7 days with or without 15 nM ALT-803 and CXCR5 messenger RNA levels were determined via quantitative RT-PCR at days 1, 3, 5, and 7 posttreatment. (D) PBMCs from 9 RMs (filled) and 3 cynomolgus macaques (open) were cultured in vitro for 5 days with or without 15 nM ALT-803. CD8+ T cells were then assessed for surface expression of CXCR5. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001.