Fig. 5.
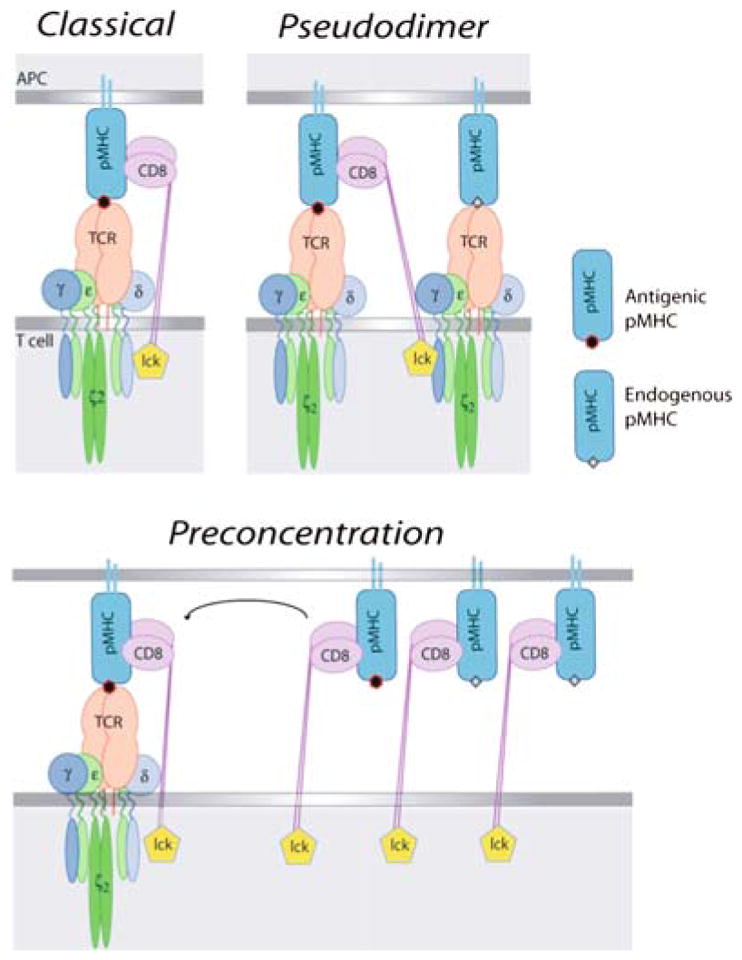
Models of co-receptor function in T-cell activation. For consistency, these are all drawn using CD8 as the co-receptor. However, the pseudodimer model (b) is derived from studies of CD4+ MHC class II-restricted T cells (Krogsgaard et al. 2005). (a) The “classical” model where the co-receptor stabilizes the interaction between TCR and antigenic MHC–peptide. (b) The “pseudodimer” model, where co-receptor cross-links two TCRs, one interacting with antigenic MHC–peptide, and the other interacting with endogenous MHC–peptide. (c) The “pre-concentration” model, where the co-receptor interaction with antigenic or nonstimulatory MHC–peptide causes concentration of MHC–peptide, co-receptor, and Lck to the synapse
