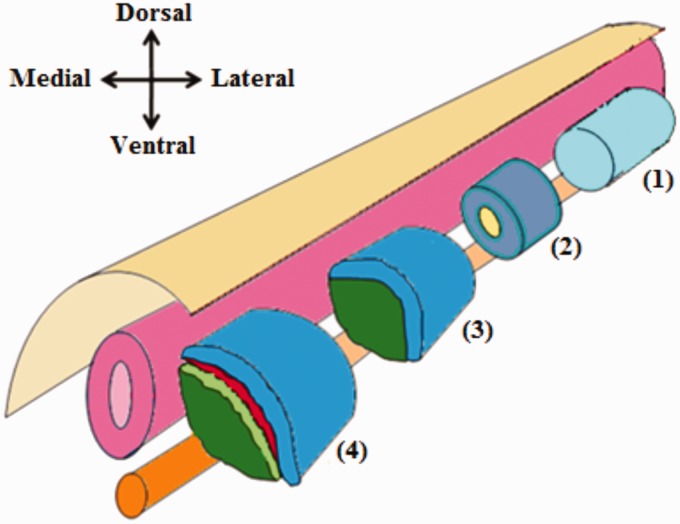
Figure 3.
Differentiation of the paraxial mesoderm. Prior to somite formation, the paraxial mesoderm is composed of a single epithelial tube which flanks the neural tube and notochord (1). Later on, the paraxial mesoderm becomes segmented into somites. Each somite consists of epithelial cells with a mesenchymal core (2). Further differentiation of each somite results in the formation of two distinct layers; the dorsolateral dermomyotome, and the ventromedial sclerotome (3). After that additional two layers formed; the myotome which derived from the dermomyotome and the syndetome which derived from sclerotome (4). (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)