Figure 8.
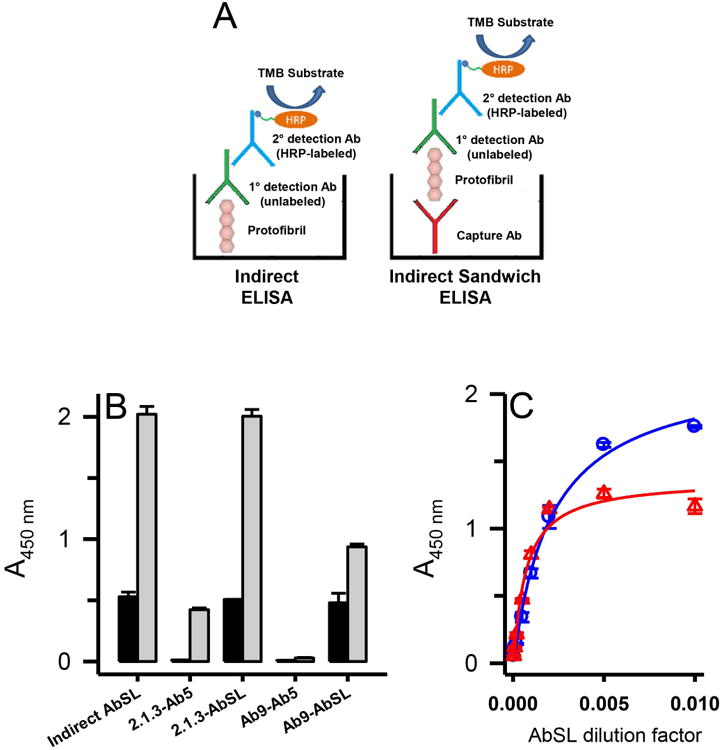
Conformational epitope on Aβ42 protofibrils for AbSL partially involves the N-terminal region. Panel A. Schematics are shown for the principal ELISA paradigms used for AbSL antibody testing, which include an indirect ELISA and an indirect sandwich ELISA. The latter system used either an HRP-conjugated Ab5 detection antibody (Terrill-Usery et al. 2016) or an HRP-conjugated secondary detection antibody when AbSL was used as the primary detection antibody. Panel B. Various combinations of capture and detection antibodies were tested in the indirect sandwich ELISA paradigm. The capture antibody is listed first and the detection antibody second (e.g. 2.1.3-Ab5). ELISA plates were coated with capture antibodies Ab2.1.3 (5 μg/mL) and Ab9 (1 μg/mL) for the indirect sandwich ELISA, which was carried out as described in the Methods. Aβ42 protofibrils (18 ng/well) were added to the capture antibodies followed by various detection antibodies. Background controls (no Aβ42) are shown in the black bars while Aβ42 samples are shown in white bars. Sample data are the mean of n = 4 replicates ± SEM. Panel C. Immunoplates were coated with capture antibodies Ab2.1.3 or Ab5 as described in Panel B. Aβ42 protofibrils (45 ng/well) were added and detected with varying dilutions of AbSL (100-20,000). Sample data are the mean of n = 3 replicates ± SEM and were fit to a 3-parameter single rectangular hyperbola equation.
