Figure 1.
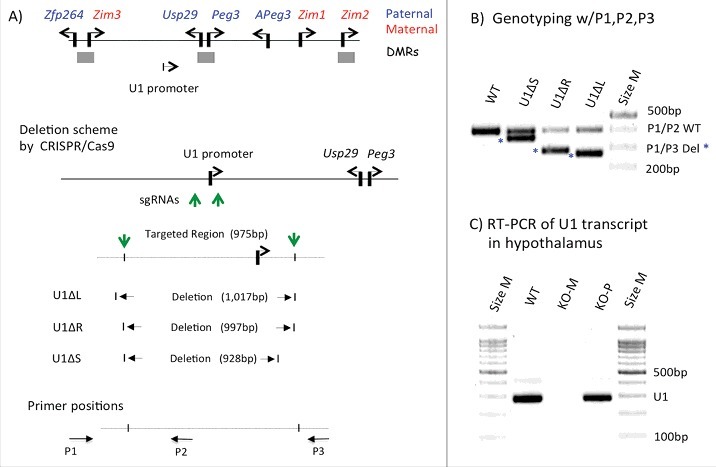
CRISPR/Cas9-based deletion of the U1 promoter. (A) Schematic representation of the Peg3 domain. Each imprinted gene is indicated with an arrow. Paternally and maternally expressed genes are indicated in blue and red, respectively. The three DMRs are indicated with gray boxes. The relative position of the U1 promoter is indicated with an arrow. The detailed genomic structure of U1 is also shown with the two single-stranded guide RNA for CRISPR/Cas9-based deletion, the positions of which are indicated with green vertical arrows. The CRISPR/Cas9-based deletion derived the three representative mutant alleles, and their deleted regions are shown. The arrows on the bottom indicate the three primers (P1, P2, P3) that were used for genotyping. (B) PCR-based genotyping of the deleted alleles. The three primers were used together for genotyping: the combination of P1 and P2 primers targets the wild type allele (403 bp in length), whereas the combination of P1 and P3 primers targets the deleted alleles (about 270 bp). (C) RT-PCR detecting the transcript driven by the U1 promoter. This series of analyses used a set of total RNA isolated from the hypothalamus of adult mice of three genotypes: WT, KO(−/+)-M, and KO(+/−)-P, the last two inheriting the deletion maternally and paternally, respectively.
