Figure 4.
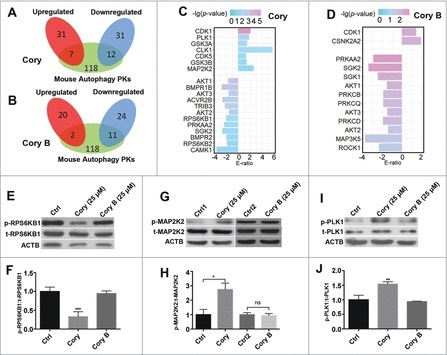
The phosphoproteome-based identification of protein kinases potentially involved in neuronal autophagy. We used the iKAP algorithm for the prediction of differentially regulated kinases (p-value < 0.05) and adopted mouse proteins annotated in THANATOS to filter potentially false positive hits for the (A) Cory and (B) Cory B groups. (C) The list of kinases differentially regulated by Cory. (D) The differentially regulated kinases induced by Cory B. (E) The total (t-) protein and phosphorylation (p-) levels of RPS6KB1 were measured to probe the RPS6KB1 activity dynamics upon Cory or Cory B treatment. (F) Cory but not Cory B decreases the phosphorylation level and the kinase activity of RPS6KB1 (***p < 0.001, Cory vs. Ctrl). (G) The total protein and phosphorylation levels of MAP2K2 were measured. (H) Cory increases the phosphorylation level and kinase activity of MAP2K2 (*p < 0.05; ns, not significant). (I) The total protein and phosphorylation dynamics of PLK1. (J) Cory increases the PLK1 activity (*p < 0.01, Cory vs. Ctrl).
