Figure 2.
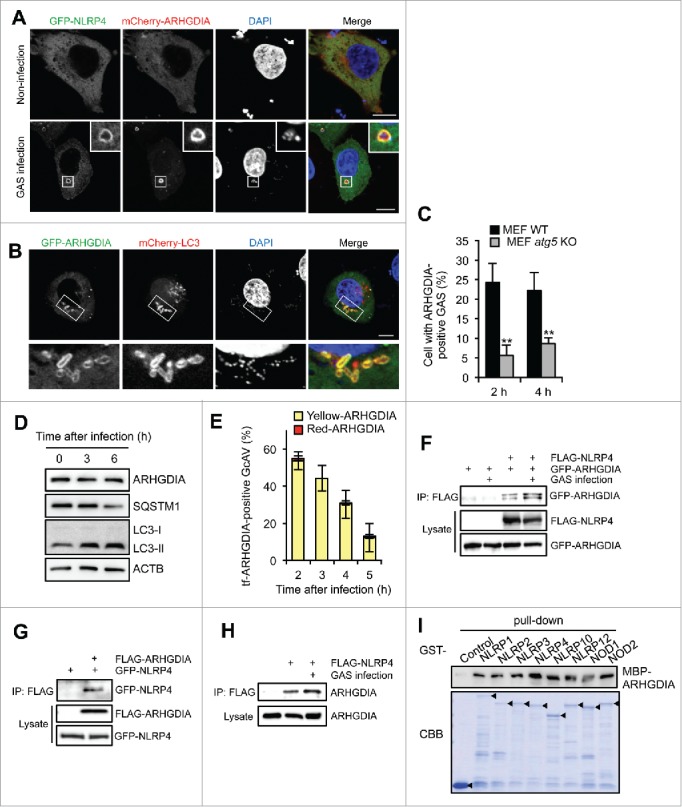
ARHGDIA interacts with NLRP4 and colocalizes with GcAV. (A) HeLa cells expressing GFP-NLRP4 and mCherry-ARHGDIA were either non-infected or infected with GAS for 2 h. (B) HeLa cells expressing GFP-ARHGDIA and mCherry-LC3 were infected with GAS for 2 h. Scale bars: 10 μm. (C) Percentage cells with ARHGDIA-positive GAS. MEF cells expressing GFP-ARHGDIA were infected GAS for 2 or 4 h. Colocalization frequencies of GAS with ARHGDI signals were manually determined. Data represent the mean ± SD (n > 100 cells, **P < 0.01) from 3 independent experiments. (D) HeLa cells were infected with GAS for the indicated times and subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (E) Quantification of GFP-mCherry-ARHGDIA (tf-ARHGDIA)-positive GcAVs at the indicated time point after infection. Data represent the mean ± SD (n > 50 GcAVs in each experiment) from 3 independent experiments. (F) HeLa cells transfected with FLAG-NLRP4, GFP-ARHGDIA, or empty vector controls were infected with GAS. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibody and immunoblotted with anti-GFP antibody. Total lysates served as input controls. (G) FLAG IPs in HeLa cells transfected with FLAG-ARHGDIA, GFP-NLRP4, or empty vector controls infected with GAS. (H) Lysates from HeLa cells transfected with FLAG-NLRP4 or empty vector and infected with GAS were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and immunoblotted with anti-ARHGDIA antibody. (I) In vitro affinity-isolation assay between MBP-ARHGDIA and GST-NLRPs. Beads carrying the indicated purified GST fusion protein were incubated with lysates from E. coli expressing MBP-ARHGDIA. CBB, Coomassie Briliant Blue.
