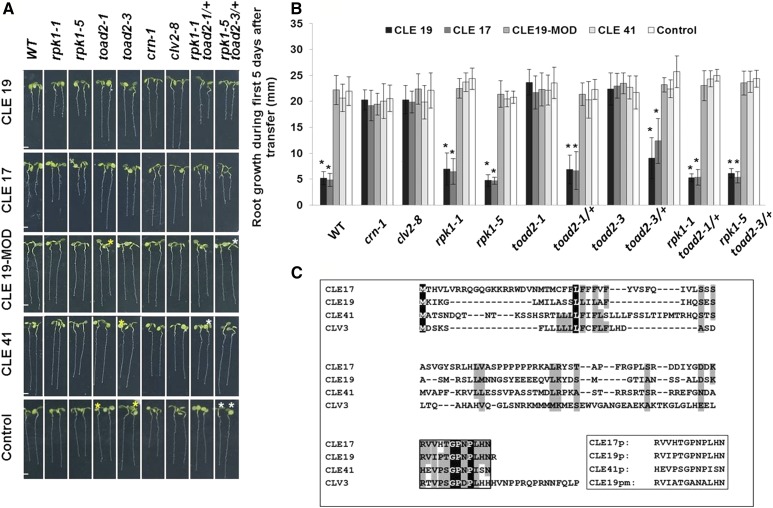
Figure 5.
Root growth sensitivity after treatment with CLE peptides. (A) Root phenotypes of rpk1, toad2, and rpk1 toad2/+ mutants, and wild-type (WT), crn-1, and clv2-8 control plants shown after 5 days of treatment with exogenous CLE peptides. Progeny of toad2/+ plants and rpk1 toad2/+ heterozygote parents were used in the assays. Plants marked with white asterisks were genotyped as rpk1 mutants only, and with yellow asterisks were WT or heterozygous for toad2. Bar, 2 mm. (B) Distribution of root lengths 5 days after transfer to CLE treatment plates. Values represent average of root length measurements in three independent experiments. Error bars represent SD (* P < 0.001; n = 8 for toad2/+; n > 16 for all other genotypes, Student’s t-test, C.I. 95%). Significant changes with CLE treatment for each genotype relative to the untreated plants are marked with *. No significant differences are observed between WT and the other untreated genotypes (long phenotypic class). (C) Alignment of Arabidopsis CLV3 amino acid sequence with sequences of CLE peptides used in this study and the synthetic peptides (box) used for the root assay. Completely conserved amino acids are shaded in black; partially conserved or highly similar amino acids (groups of strongly similar properties scoring >0.5 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix ClustalW) are shaded in gray; and the conserved CLE motif is framed.