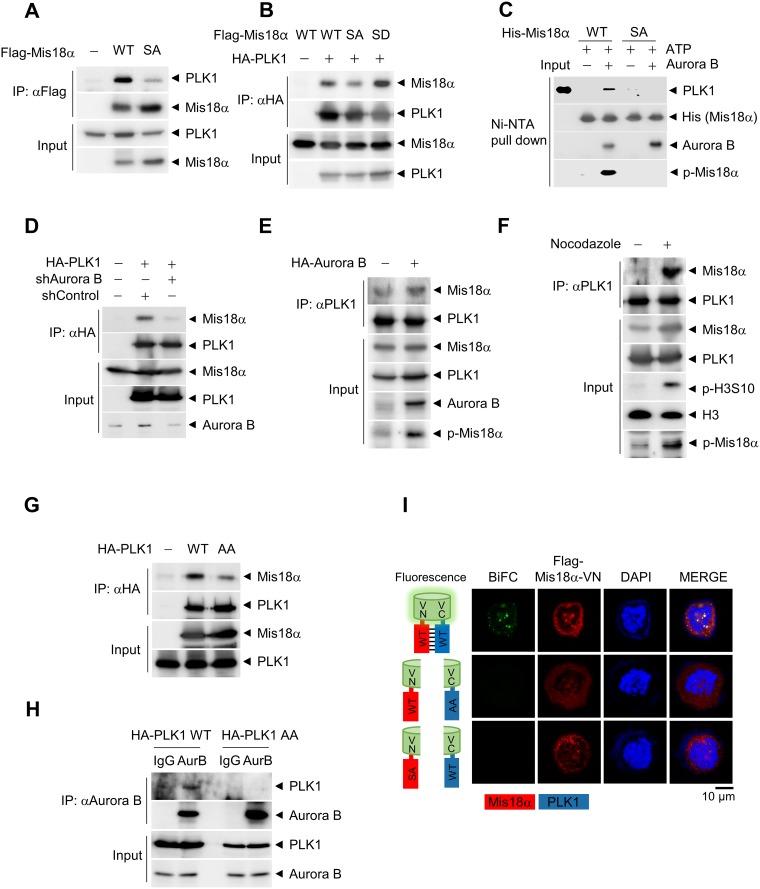
Figure 5. PLK1 recognizes Mis18α phosphorylation through its PBD.
(A) Flag-Mis18α and HA-PLK1 constructs were transfected in 293T cells and cell extracts were applied for IP analysis by using anti-Flag antibody. (B) Flag-Mis18α and HA-PLK1 constructs were transfected in 293T cells and cell extracts were applied for IP analysis by using anti-HA antibody. (C) HA-PLK1 was synthesized in vitro by using a coupled Transcription/Translation system and incubated with recombinant His-Mis18α in the presence of Aurora B kinase for in vitro binding assay. The sample was subjected to immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody. (D) 293T cells were transfected as in A in the presence or absence of shRNA against Aurora B kinase. IP was performed by using anti-HA antibody. (E–F) Flag-Mis18α constructs were transfected in 293T cells in the presence of Aurora B kinase overexpression (E) or nocodazole treatment (F), and IP was performed by using anti-PLK1 antibody. (G) Flag-Mis18α was transfected into 293T cells together with either wild-type PLK1 (HA-PLK1 WT) or PBD-mutant form of PLK1 (HA-PLK1 AA). IP was performed using anti-HA antibody. (H) 293T cell extracts expressing either HA-PLK1 WT or HA-PLK1 AA were applied for IP analysis using anti-Aurora B kinase antibody. (I) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay. Flag-Mis18α-VN constructs and HA-PLK1-VC constructs were transfected into HeLa cells and the fluorescence images were detected under confocal microscope (green fluorescence for BiFC and red fluorescence for Mis18α). Confocal image with 1,000× magnification.