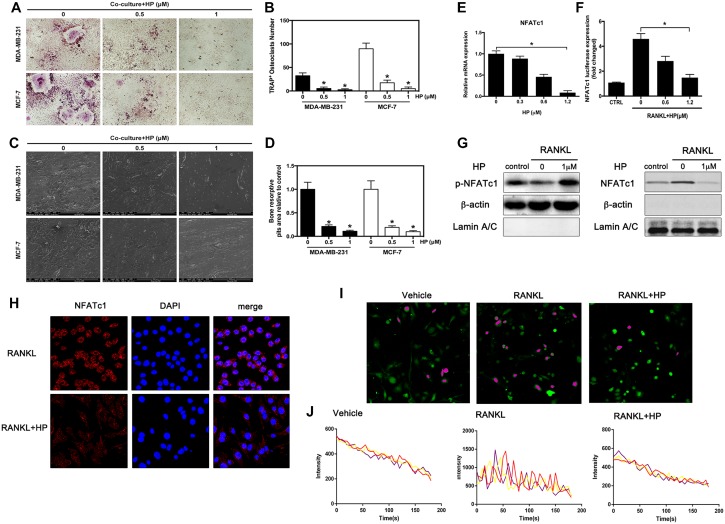
Figure 2. Hypericin inhibits breast cancer-induced osteoclast differentiation and function via suppression of the NFATc1 signaling pathway and attenuation of Ca2+ oscillation in osteoclasts.
(A) RAW264.7 cells (3 × 103 cells/well) were incubated in the presence of MCF-7 or MDA-MB-231 cells for 24 h, exposed to HP (1 μmol/L) for 5 days, and finally stained for measurement of TRAP expression. (B) Multinucleated osteoclasts (> 3 nuclei) in co-cultures were counted. Columns represent the mean results of experiments carried out in triplicate, whereas bars represent the SD. (C) HP-inhibited osteoclast bone resorption induced by tumor cells. RAW264.7 cells (3 × 103 cells/well) were seeded into bovine bone slices in the presence of MCF-7 or MDA-MB-231 cells for 24 h, and treated with HP (1 μmol/L) for 5 days. After 5 days of incubation, images were obtained using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Images of bone resorption pits are shown. (D) Resorption pit areas were measured using ImageJ software. Columns represent the mean results of experiments carried out in triplicate, whereas bars represent the SD. (E) RAW264.7 cells were incubated in serum-free media containing the indicated concentrations of HP and RANKL for 24 h. The cells were lysed, and total RNA was subjected to RT-PCR for determination of NFATc1 gene expression. Graphs indicate the relative intensity of NFATc1 compared to that of GAPDH. (F) RAW264.7 cells that were stably transfected with a NFATc1 luciferase reporter construct were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of HP for 1 h and then incubated in the absence or presence of RANKL for 12 h. Luciferase activity was then determined using the Promega luciferase assay system. (G) RANKL-induced NFATc1 translocation to the nucleus was assessed by western blotting. RAW264.7 cells (1 × 106 cells/well) were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of HP for 2 h and then stimulated with RANKL (50 ng/mL) or were untreated (controls) for 15 min. Cell nuclear extracts were prepared and subjected to western blotting using anti-NFATc1 and LaminA/C. Cell cytosol extracts were prepared and subjected to western blotting using anti-phospho-NFATc1 and actin. (H) Effects of HP on nuclear translocation of NFATc1 in RAW264.7 cells. Cells were treated with RANKL for 72 h in the presence and absence of HP (1 mmol/L) and stained with anti-NFATc1 antibody to investigate NFATc1 nuclear translocation (left panel). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (middle panel). Merged images of NFATc1 and the nuclei are shown in the right panel. (I) HP reduces intracellular Ca2+ levels and calcium influx. RAW264.7 cells (3 × 103 cells/well) were incubated with RANKL (100 ng/mL) in the presence or absence of HP (1 μM) for 72 h. For Ca2+ measurement, cells were incubated with Fluo-4 AM and 0.05% pluronic F-127 (Invitrogen) in HBSS supplemented with 1% FCS and 1 mM probenecid (assay buffer) for 30 min followed by confocal analysis. Representative fluo-4 fluorescent images of the RAW264.7 cells from different treatment groups are shown. Pseudo-color-labeled (purple) area represents the cells that are actively undergoing fluorescence ratio changes. (J) The relative intracellular Ca2+ levels in individual cells were monitored for 5 min at 5-second intervals using the fluorescence intensity of Fluo-4 at 200× magnification. Cells with at least two oscillations were counted as oscillating cells. A minimum of 40 cells were monitored in triplicate wells. The average amplitude of Ca2+ oscillations in each cell was calculated using the TuneR and SeeWave packages for the R programming language. Representative traces of three randomly chosen BMMs were recorded in different treatment groups. The fluorescence ratio change was recorded every 5 s for 300 s.