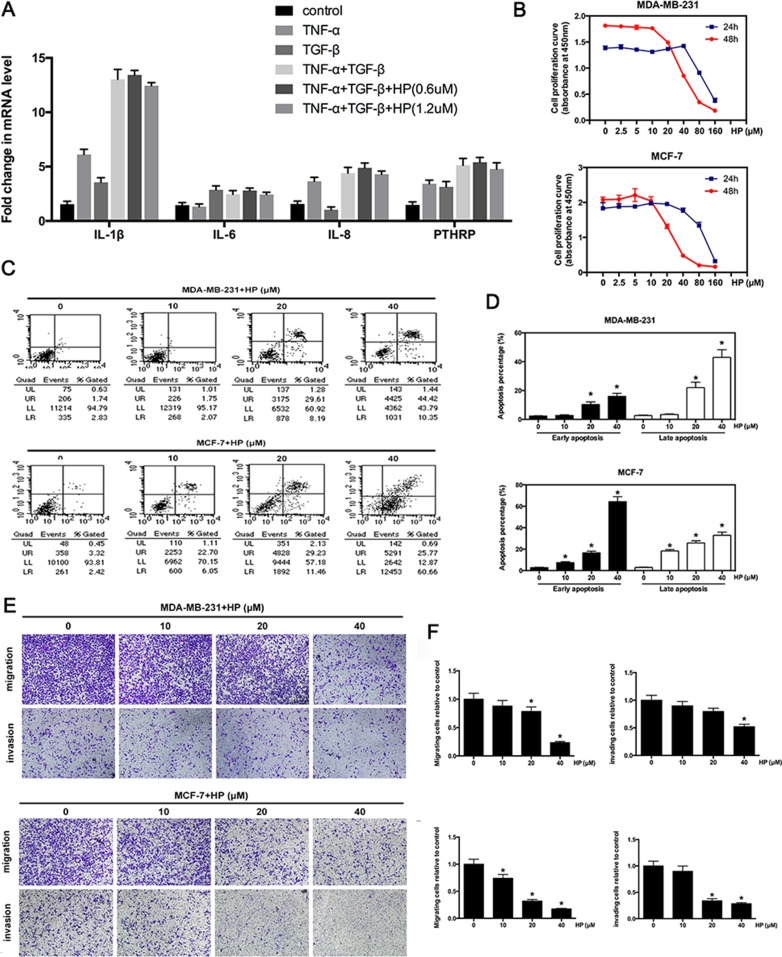
Figure 4. Hypericin inhibits the expression of osteoclast-activating factors and suppresses the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells.
(A) Effects of HP on the expression of osteoclast-activating factors induced by bone microenvironment cytokines. After pretreatment with the indicated concentrations of HP for 6 h, MDA-MB-231 cells (2 × 105 cells/well) were stimulated with TNF-α (0.1 nM) or TGF-β (5 ng/mL), or TNF-α with TGF-β for 2 h. Total RNA was collected and subjected to quantitative real-time PCR using the indicated primers. (B) Effects of HP on the viability of breast cancer cells. MDA-MB-231 cells (8 × 103 cells) and MCF-7 cells (8 × 103 cells) were treated with the indicated concentrations of HP for 24 and 48 h. Cell viability was determined by the CCK8 assay. (C) HP promotes apoptosis at high concentrations. Flow cytometric analysis of HP-treated MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells. (D) Percentage of apoptotic MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells. Quantitative analysis of the percentage of apoptotic cells after 48-hour incubation. (E) Effects of HP on the inhibition of breast cancer cell migration and invasion. MDA-MD-231 and MCF-7 cells were starved for 12 h, and then seeded in the top chambers of transwells either with matrigel (for the invasion assay) or without matrigel (for the migration assay) in the presence of the indicated doses of HP. The bottom chambers of the transwells were filled with the a medium containing 10% FBS. Cancer cells were allowed to migrate for 6–8 h or invade for 10–12 h. The purple-stained cells, which migrated and invaded, showing irregular shape were photographed and counted. (F) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of cell migration and invasion using ImageJ. Columns represent the means of experiments performed in triplicate, whereas bars represent the SD.