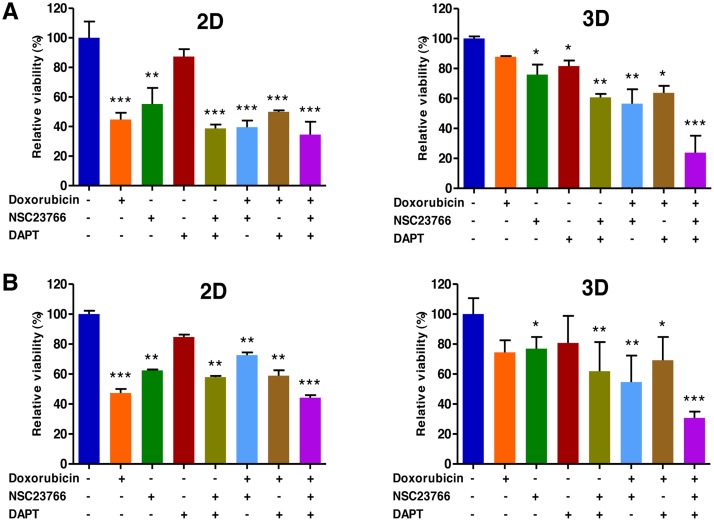
Figure 8.
Combined targeting of Tiam1 and Notch synergistically increase sensitivity to doxorubicin in 2D- and 3D-cultured EL4 T (A) and A20 (B) B lymphoma cells. (A) WST-1-based colorimetric cell cytotoxicity assay demonstrates a significant difference between 2D and 3D cultures with regard to doxorubicin sensitivity. The levels of increased sensitivity to doxorubicin in the group pretreated with either the Tiam1/Rac1 inhibitor or the Notch inhibitor compared to the group treated with doxorubicin alone are significantly higher in 3D than in 2D condition in both cell types. The levels of increased sensitivity to doxorubicin in the group pretreated with a combination of Tiam1 and Notch inhibitors compared to the group pretreated with either the Tiam1/Rac1 inhibitor or the Notch inhibitor are much higher in 3D than in 2D condition in both cell types. Remarkably, the augmented sensitivity to doxorubicin by combined pretreatment with Tiam1 and Notch inhibitors is more prominent in 3D lymphoma spheroids compared to the 2D-cultured cells in both cell types. Data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 versus the control.