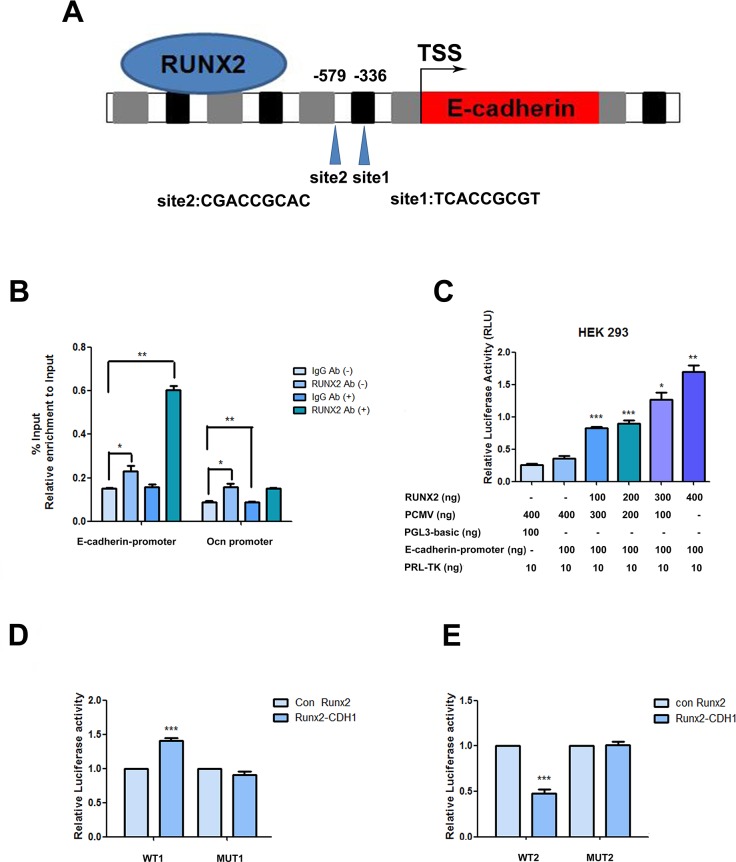
Figure 5. RUNX2 direct regulation on the promoter.
(A) Schematic diagram of the human E-cadherin gene promoter showing the positions of potential binding sites of putative transcription factor RUNX2 analyzed using Jarsper. Two segments at -336 bp (site1) and -579 bp (site2) upstream from the transcription start site (TSS). (B) Binding of RUNX2 to the E-cadherin promoter region in ADSCs cultured with epithelial differentiation medium or control (-) were detected by chromatin immunoprecipitations. Protein-chromatin crosslinked complexes were immunoprecipitated with either RUNX2 antibody or negative control antibody IgG. Chromatin immunoprecipitate obtained in the ChIP assay was quantified by real-time PCR. PCR primers spanning E-cadherin promoter including the three putative binding sites regions were employed. OCN promoter primers were used as a positive control. The data show promoter occupancy normalized to Input and represent Mean ± SD of three independent experiments, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (C) Activity of the E-cadherin promoter in ADSCs co-transfected with the indicated amounts of pCMV-RUNX2 plasmid, pGL3- E-cadherin promoter and pRL-TK. Dose dependent increase of E-cadherin promoter activity in ADSCs with increasing concentration of pCMV-RUNX2 plasmid was measured by dual-luciferase assay. Luciferase values expressed were normalized with respect to pRL-TK value. (D) Induced ADSCs were transfected with pCMV vector, pCMV-RUNX2, siRNA or siRUNX2 respectively for 48 h. Total cell lysates obtained from these cells were assayed for luciferase activity and normalized with pRL-TK activity co-expressed in these cells. (E) Induced ADSCs were transfected with pCMV vector, pCMV-RUNX2, siRNA or siRUNX2 respectively for 48 h. Total cell lysates obtained from these cells were assayed for luciferase activity and normalized with pRL-TK activity co-expressed in ADSCs. Data represent triplicate studies with a mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. Each experiment was repeated at least three times.