Figure 7.
Recombination at Dysfunctional Chromosome Ends
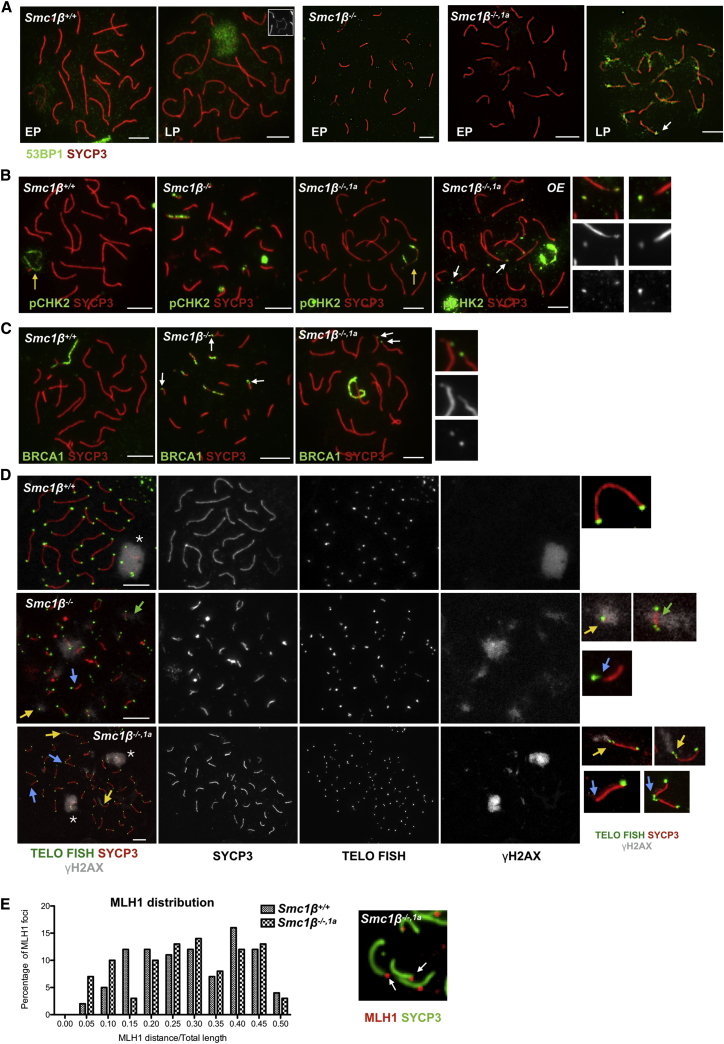
(A) Spermatocyte chromosome spreads of Smc1β+/+, Smc1β−/−, and Smc1β−/−,1a mice, stained with anti-SYCP3 for AEs/LEs and with anti-53BP1 for DNA repair protein (EP, early pachynema; LP, late pachynema). White arrow shows accumulation of 53BP1 at the end of the chromosome.
(B) Spermatocyte chromosome spreads of Smc1β+/+, Smc1β−/−, and Smc1β−/−,1a mice, stained with anti-SYCP3 for AEs/LEs and with anti-pCHK2. OE indicates over-exposed image of Smc1β−/−,1a spermatocyte. White arrow shows accumulation of phosphorylated CHK2 at the end of the chromosome. Yellow arrow indicates sex chromosomes. Magnified images show phosphorylated CHK2-positive chromosome ends.
(C) Spermatocyte chromosome spreads of Smc1β+/+, Smc1β−/−, and Smc1β−/−,1a mice, stained with anti-SYCP3 for AEs/LEs and with anti-BRCA1 for DNA repair protein. White arrow shows accumulation of BRCA1 at the end of the chromosome. Magnified images show BRCA1-positive chromosome ends.
(D) Chromosome spreads stained for telomere by telo-FISH (green), with anti-SYCP3 for AEs/LEs and with anti- phosphorylated H2AX (γH2AX) for DNA damage. Magnified images show normal and dysfunctional telomeres. Yellow arrow indicates γH2AX-positive dysfunctional telomere. Blue arrow indicates γH2AX-negative dysfunctional telomere. Green arrow shows γH2AX-positive asynapsed chromosome.
(E) Graphical representation of MLH1 distribution along the chromosome of Smc1β+/+ and Smc1β−/−,1a spermatocytes. White arrows in the magnified image of Smc1β−/−,1a spermatocyte show MLH1 at the end of chromosome. According to Chi-square analysis, the histograms of Smc1β+/+ and Smc1β−/−,1a spermatocytes are not statistically significantly different; p = 0.2644 (scale bar, 5 μm).
See also Figure S7.