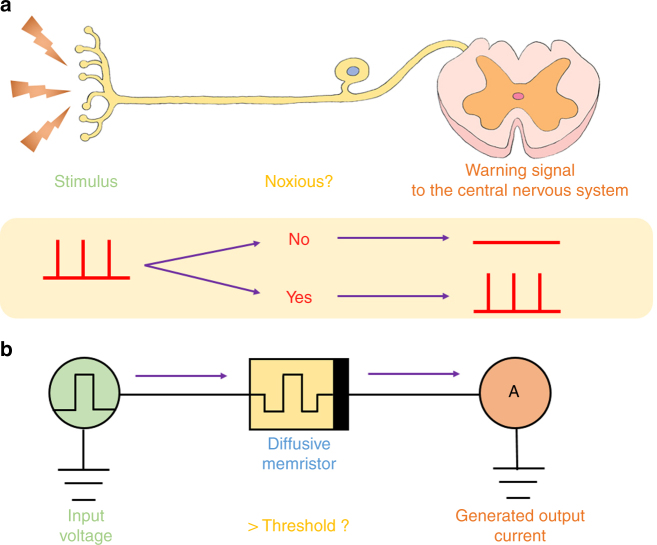
Fig. 1.
One to one correspondence of the nociceptor system in the human body and an artificial nociceptor circuit consisting of a diffusive memristor (threshold switch). a When a noxious stimulus is received from a free nerve ending, the nociceptor compares the amplitude of the signal with a threshold value and decides whether an action potential should be generated and sent to the brain via the spinal cord (central nervous system). b An electrical pulse applied on the device emulates the external stimulus. When the pulse amplitude is higher than the threshold voltage of the diffusive memristor, the device is turned ON, and current pulses are generated