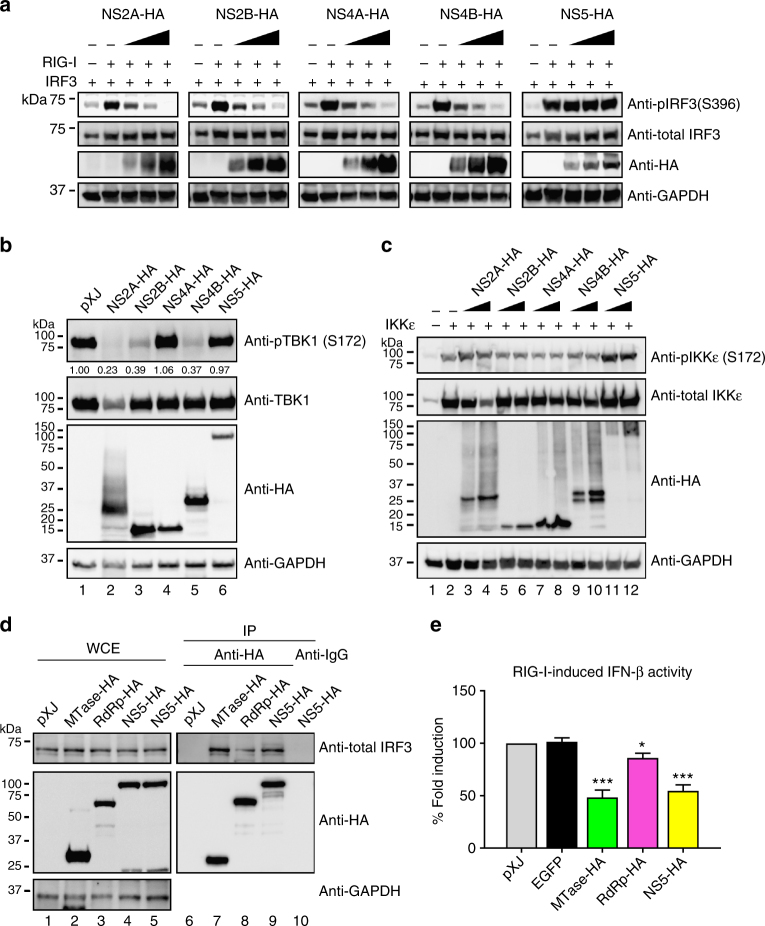
Fig. 2.
ZIKV non-structural proteins inhibit TBK1s and IRF3 activation. HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with IRF3-expressing plasmid together with RIG-I(2CARD)-coding plasmid (a), TBK1-expressing plasmid (b), or IKKε-expressing plasmid (c), as well as ZIKV non-structural protein-expressing plasmid or empty vector plasmid. Cells were harvested at 24 h post-transfection and subjected to western blotting with indicated antibodies, phosphorylated IRF3 (anti-pIRF3 S396), total IRF3 (anti-IRF3), phosphorylated TBK1 (anti-pTBK1 S172), total TBK1 (anti-TBK1), phosphorylated IKKε (anti-pIKKε S172), total IKKε (anti-IKKε), GAPDH (anti-GAPDH), and ZIKV proteins (anti-HA). All viral proteins were cloned from the pre-epidemic, Cambodian strain ZIKV (FSS13025) isolated from a patient in 2010. d Co-immunoprecipitation of NS5 and IRF3. HEK-293T cells were transfected with HA-fused MTase-, RdRp-, or full-length NS5-expressing plasmid and RIG-I(2CARD) stimulating plasmid. At 24 h post-transfection, cells were harvested and whole-cell extracts (WCE) were loaded as input (left panel). WCE were used for immunoprecipitation using anti-HA beads or anti-mouse IgG as a negative control, followed by detection of IRF3 using anti-total IRF3 antibody (right panel). The levels of proteins were quantitated by band intensity using Image lab software (BioRad). For a–d, the original uncropped blots can be found in Supplementary Fig. 5. e Luciferase assay of IFN-β promoter. MTase-, RdRp-, or NS5-expressing plasmid was co-transfected with RIG-I (2CARD) and reporter plasmids to HEK-293T cells. Cells were assayed for luciferase signals at 24 h post-transfection. Data are shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s two-sided t-test, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, or no significance (n.s.)