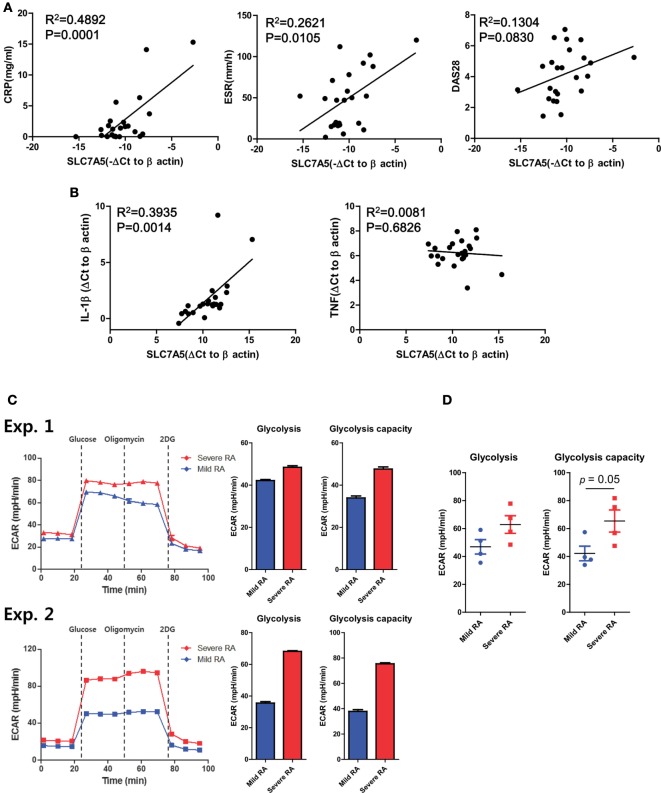
Figure 6.
Clinical relevance of increased SLC7A5 expression on monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. (A) Correlation between SLC7A5 gene expression and RA clinical parameters in peripheral monocytes (n = 24). Expression was normalized to β-actin and ΔCt was calculated by subtracting the Ct of β-actin from the Ct of SLC7A. The relative gene expression of SLC7A5 is plotted against ESR, CRP, and DAS28. (B) Correlation of SLC7A5 gene expression in peripheral monocytes with IL-1β or TNF-α gene expression in RA patients (n = 23). p Values were obtained using the Pearson correlation analysis (A,B). (C) Real-time extracellular acidification rate (ECAR), glycolysis, and glycolysis capacity in monocytes derived from clinically mild or severe RA patients. ECAR levels were measured following sequential treatments with glucose (10 mM), oligomycin (2 µM), and 2-DG (50 mM). (D) Scatter plots show glycolysis and glycolysis capacity in peripheral monocytes of mild (n = 4) or severe RA patients (n = 4). *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 by two tailed unpaired t-test (C,D).