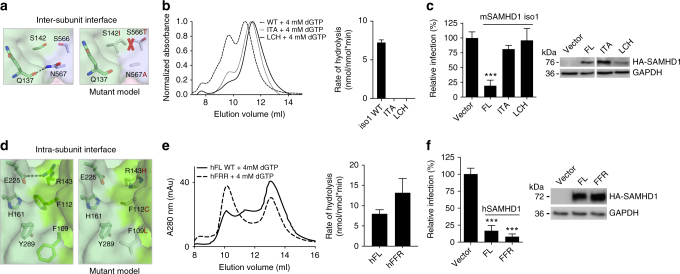
Fig. 3.
The importance of SAM-to-HD interactions for mSAMHD1 oligomerization and activities. a, d Left, transparent surface representation of SAM-to-HD interface with important residues shown in sticks. Right, model of SAM-to-HD interface after mSAMHD1 residues are mutated to the corresponding hSAMHD1 residues. The red cross in a indicates a steric clash. b, e Left, SEC analysis of mSAMHD1 (b) or hSAMHD1 (e) variants before and after incubation with dGTP-α-S. Right, dNTPase assay for wild type and mutant mSAMHD1 proteins (b) or hSAMHD1 (e). Products were quantified by the malachite green assay. Each experiment was performed in triplicate. Error bars, s.d. c, f HIV-1 restriction by full-length mSAMHD1 iso1 (c) or hSAMHD1 (f) (WT and mutants) stably expressed in U937 cells after PMA differentiation. Immunoblotting (uncropped images in Supplementary Fig. 7) confirmed HA-tagged mSAMHD1 or hSAMHD1 expression. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Single-cycle HIV-1 infection of vector control cells was set as 100%. Each experiment was performed in triplicate. Error bars, s.d. ***p ≤ 0.0001