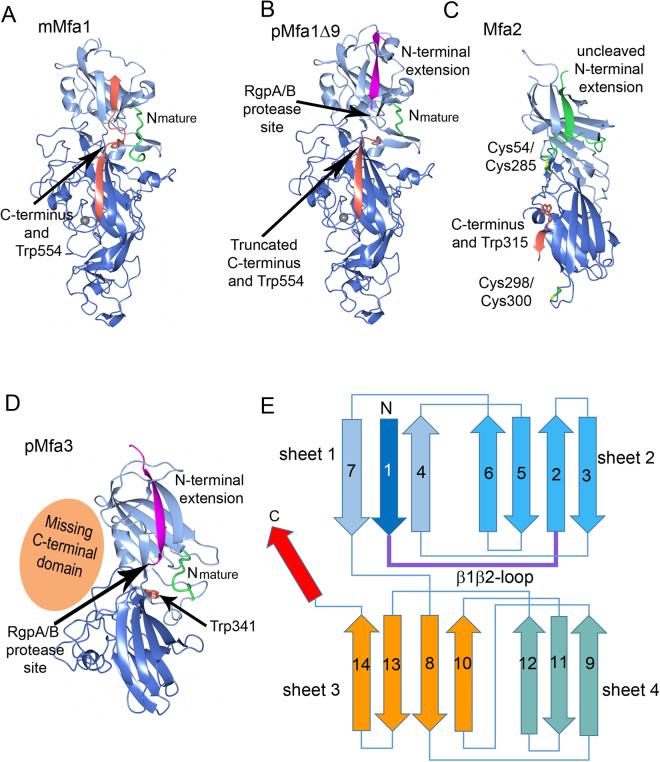
Figure 2.
Overall structures of Mfa1, Mfa2 and Mfa3. (A) The mature form of Mfa1 with the full-length C-terminus located in the first β-sheet (mMfa1). (B) The precursor form of Mfa1 with the final nine amino acid residues removed (pMfa1Δ9). (C) The structure of Mfa2. (D) The structure of the truncated Mfa3 with the missing C-terminal domain depicted as an orange sphere (pMfa3). The RgpA/B cleavage sites are marked with arrows in (B) and (D). The cleavable N-terminal extensions (β1-strands) are depicted in magenta in pMfa1Δ9 and Mfa3, and the uncleavable N-terminal extension in Mfa2 in green. Nmature is shown in green (pMfa1Δ9, mMfa1 and pMfa3) and the C-terminal strand in mMfa1 is shown in orange. The structurally conserved tryptophan residue located between the N- and C-terminal domains are depicted as orange stick models in all structures. In Mfa2 the two disulphide bonds are shown as stick models. (E) Overall topology of the Mfa proteins: an N-terminal domain and a C-terminal domain consisting of two sheets each (sheets 1 and 2 and sheets 3 and 4, respectively). Upon maturation the β1β2-loop is cleaved and the β1-strand is removed. The C-terminal β-strand, depicted in red, is present in several of the Bacteroidetes fimbrial shaft proteins and can adopt different conformations.