FIG 7.
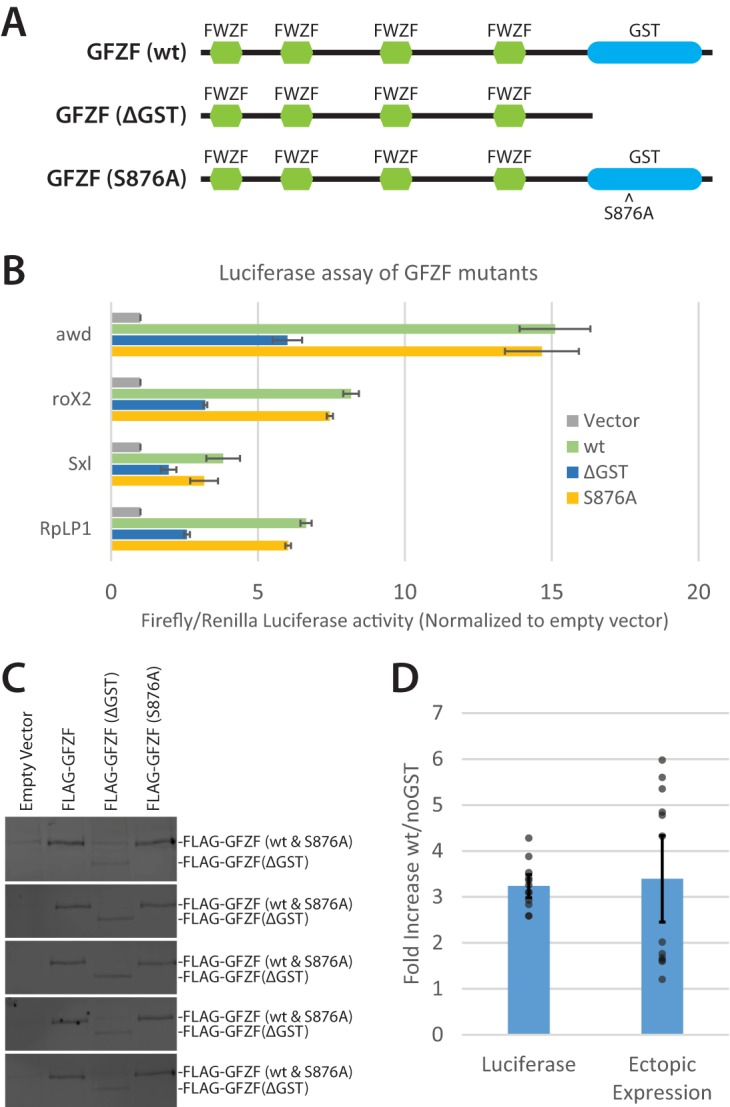
GFZF's GST domain is not required for transcription activation of transfected DNA. (A) Schematic of GFZF and mutations used to test the function of GFZF's GST domain in transcription activation. FWZF stands for FLYWCH zinc finger domain. (B) Normalized firefly/Renilla luciferase activities are displayed for four different reporter promoters with wt, ΔGST, and S876A mutant versions of GFZF ectopically expressed (n = 3). (C) Representative Western blots of luciferase lysates following ectopic expression of wt, ΔGST, or S876A GFZF. Western blots from 5 of 12 independent experiments are shown. The upper and lower band in each blot correspond to full-length (wt or S876A) and truncated (ΔGST) GFZF, respectively. The wt and ΔGST bands were quantified with ImageJ to determine the fold difference in ectopic expression. (D) Fold differences in luciferase activity and ectopic GFZF expression are compared for the wt and ΔGST GFZF samples after combining the data for all four of the tested promoters. Calculation of the ratio of activation by wild-type and ΔGST GZF was made by subtracting the endogenous (empty vector) luciferase values from the values for ectopically expressed GFZF samples and then taking the ratio of the wt to ΔGST adjusted values. Calculation of the ratio of levels of ectopically expressed wild-type and ΔGST GFZF was made by measuring the intensities of anti-FLAG Western blot signals. There is no significant difference between the fold increase in luciferase activity and the fold increase in ectopic expression for the wt versus ΔGST samples (P = 0.78). Error bars represent standard deviation; n = 12 (3 replicates from 4 promoters).
